LONDON: In the early hours of Sunday, Dec. 8, shortly after a coalition of opposition forces seized Damascus and toppled Bashar Assad’s regime, Israeli troops infringed on Syrian territory for the first time in 50 years, marking another breach of international law.
They advanced into a demilitarized zone along the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights and seized roughly another 400 square kilometers of Syrian territory.
The move has drawn international criticism, with Jordan slamming the deployment of Israeli troops in the Golan as a violation of international law.
Similarly, Saudi Arabia condemned the move, saying it confirms Israel’s “determination to sabotage Syria’s chances of restoring its security, stability and territorial integrity.”
Other countries in the region, including Iran, Iraq, the UAE, Qatar, and Turkiye, also denounced Israel’s land grab in Syria. Qatar described it as “a dangerous development and a blatant attack on Syria’s sovereignty and unity.”

Israel’s foreign ministry responded with a statement accusing Turkiye of taking control of about 15 percent of Syria’s territory through three military operations from 2016 onward, and establishing armed proxy groups to control this territory, where “Turkish currency is in use, and Turkish bank branches and postal services have been operating.”
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu defended the takeover of the buffer zone as a decision taken to prevent “any hostile force from establishing itself on our border.”
He made the announcement from the Golan Heights, saying the fall of the Assad regime had rendered a Syria-Israel disengagement agreement dating back to 1974 obsolete and that “Syrian forces have abandoned their positions.”
Media reports, as well as the UK-based Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (SOHR), noted that Syrian forces abandoned their positions in Quneitra province — part of which lies within the buffer zone — just hours before Assad’s fall.
Antonio Guterres, UN secretary-general, insisted on Thursday that the 1974 agreement “remains fully in force,” calling on both Israel and Syria to uphold its terms.
Under that agreement, a UN-monitored demilitarized zone separated the Israeli-occupied territory from the area controlled by Syria.
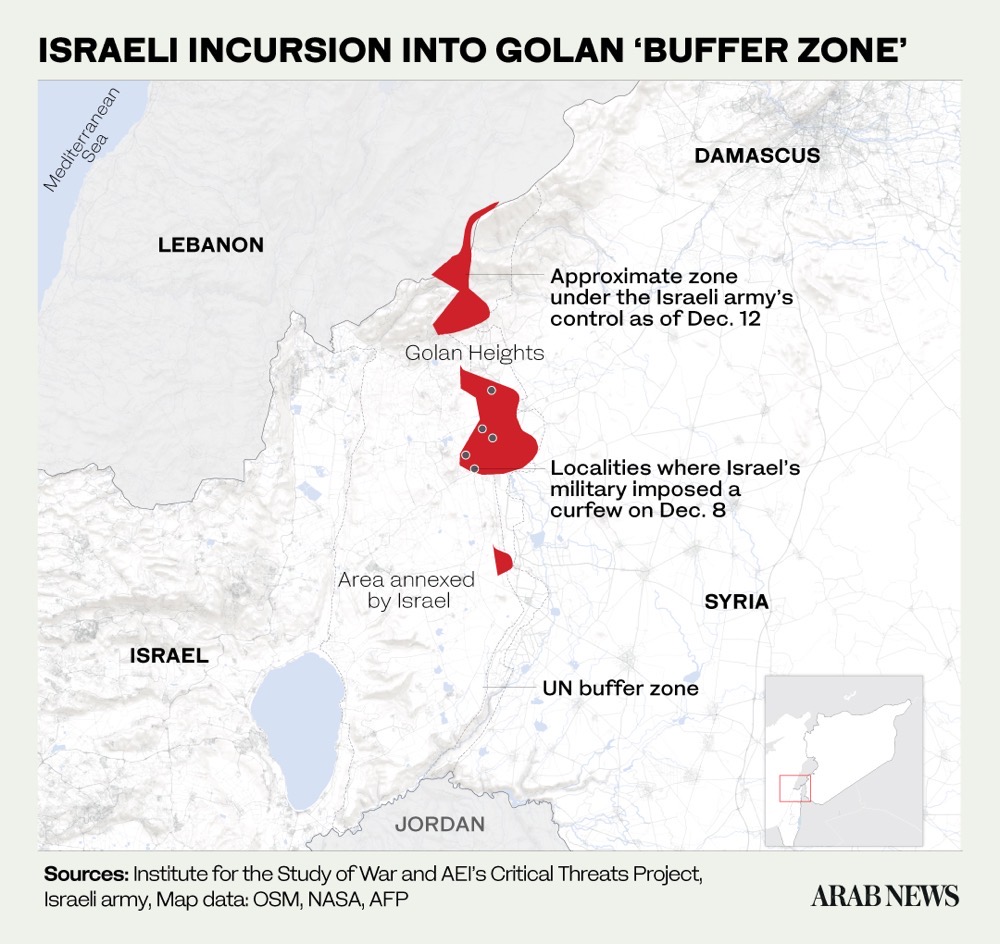
The UN criticized Israel’s capture of the buffer zone, saying it constituted a violation of the 1974 agreement. Stephane Dujarric, spokesperson for Guterres, said on Dec. 9 that “there should be no military forces or activities in the area of separation.”
The Golan Heights is a rocky plateau 60 kilometers southwest of Syria’s capital, Damascus. It abuts Mount Hermon, also known as Jabal Al-Sheikh, the highest mountain on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, according to Encyclopaedia Britannica.
Israel seized the Golan from Syria in the closing stages of the 1967 Arab-Israeli war, later thwarted a Syrian attempt to retake it during the 1973 Middle East war, and unilaterally annexed it in 1981 — a move that was not recognized by the international community.
Following Assad’s downfall on Dec. 8, the Israeli military also seized control of the highest peak of Mount Hermon on the Syrian side.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
This strategic summit, located just over 35 kilometers from Damascus and straddling the border between Syria and Lebanon, offers a commanding vantage point and firing range over the surrounding ridges, making it a crucial asset for observation and defense.
Michael Mason, director of the Middle East Centre at the London School of Economics (LSE), believes the occupied Golan Heights “is a strategically important area for Israel because of its geographical location and topography.”

“The elevation of the Golan contributes significantly to Israel’s military and surveillance capabilities in the north,” he told Arab News.
“It is not surprising, therefore, that the Israeli military seized the Syrian side of Jabal Al-Shaykh (Mount Hermon) earlier this month, and Israel has unilaterally occupied the UN-monitored demilitarized zone created in 1974.”
He added: “Politically, occupation of the Golan feeds the ultra-nationalist agenda of a Greater Israel and will encourage claims for further territorial expansion.”
Firas Modad, a Middle East analyst and founder of Modad Geopolitics, agrees that by seizing the Golan and Mount Hermon, Israel has “expanded its high grounds.”
By grabbing the highest peak of Mount Hermon, the Israelis now “overlook pretty much the entire region,” which “helps them with things like detecting drones and being able to do aerial surveillance a little bit better,” he told Arab News.
“It means that drones coming in from Iraq or from Lebanon are easier to detect for them.”
FASTFACTS
• The Golan Heights is considered occupied under international law and UN resolutions since 1967.
• In 2019, the US officially recognized Israeli sovereignty over the occupied Golan Heights.
• Syria’s attempt to retake the Golan in the 1973 Arab-Israeli war was thwarted. • There are more than 30 Israeli settlements in the occupied Golan Heights.
Modad added that capturing the Golan Heights also puts Damascus in an “untenable military position” for Israel as the Syrian capital becomes “closer to artillery range.”
He believes this places “the new government in Syria” in “an extremely vulnerable position.”
Ahmed Al-Sharaa, head of the new Syrian administration, said in an interview with The Times on Monday that war-weary Syria remains “committed to the 1974 agreement and we are prepared to return the UN (monitors).”
“We do not want any conflict whether with Israel or anyone else and we will not let Syria be used as a launchpad for attacks,” he added. “The Syrian people need a break, and the strikes must end, and Israel has to pull back to its previous positions.”
According to media reports, the Israeli military launched about 600 strikes across Syria in roughly eight days following the ousting of Assad. The Times of Israel news website reported that the Israeli military estimated it had destroyed 80 percent of the former regime’s strategic military capabilities.

More than 13 years of war and economic hardship have eroded Syria’s infrastructure and pushed 90 percent of the population below the poverty line, according to UN figures.
Some analysts warn that it could take 10 years for Syria to return to its 2011 GDP level and up to two decades to fully rebuild, Deutsche Welle reported.
The Golan Heights area is also known for its fertile land and vital water sources, including the Yarmouk River, which feeds the Jordan River.
Modad, the Middle East analyst, said Israel’s occupation of the area ensures its control over critical waterways.
“The key story is the Israelis gaining full control over the Yarmouk,” he said. “Yarmouk feeds into the Jordan River — it essentially becomes the Jordan River. It’s the river’s main tributary.”
He added: “And so, what the Israelis have done is that they’ve seized a very important water resource from the Syrians and placed it completely under their control,” giving them “leverage over Jordan by being able to cut off the water supply.”
Netanyahu stated on Dec. 9 that the Syrian Golan “will be part of the State of Israel for eternity,” despite initially describing his army’s presence in the buffer zone as “a temporary defensive position until a suitable arrangement is found.”
This territorial expansion, according to Modad, also increases Israel’s control over the Syria-Lebanon border, enhancing its ability to monitor and control traffic between the two countries.
“If they (the Israelis) keep going down the slopes of the East Lebanon mountain, that puts them in a very advantageous position to besiege Hezbollah,” the Lebanese militant group that has been fighting Israel since the 1980s.
“And the expanded territory that they’ve taken means they are much higher than Hezbollah in parts of Lebanon, including Shebaa, Rashaya and Hasbaya, all the way to the western Bekaa.”

This, he added, enhances the Israelis’ “ability to survey Hezbollah’s weapons transfers as part of their more aggressive enforcement of (Resolution) 1701 and of the ceasefire agreement,” which was signed on Nov. 27 to end the Israel-Hezbollah conflict that began on Oct. 8, 2023, and escalated into a deadly Israeli bombing campaign across Lebanon.
On Dec. 15, Netanyahu announced that his government had approved the “demographic development” of the occupied Syria territory, aiming to double the Israeli population there.
About 31,000 Israeli settlers live in dozens of illegal settlements in the Golan, alongside Syrian minority groups, including some 24,000 Druze, according to a Foreign Policy report.
A 2010 research by the Israeli daily Haaretz found that during the 1967 Arab-Israeli war and in the aftermath, some 130,000 Syrians fled or were expelled from the Golan by the Israeli army.
“Strengthening the Golan is strengthening the State of Israel, and it is especially important at this time,” Netanyahu said. “We will continue to hold onto it, cause it to blossom, and settle in it.”
LSE’s Mason believes that with the planned expansion of Israeli settlements, “the indigenous Arab population of the occupied Golan Heights — most of whom still identify as Syrian and have rejected Israeli citizenship — are likely to face intensified social and economic discrimination; for example, further loss of land and water resources.”
On Dec. 19, Israeli forces set up a position at an abandoned Syrian army base in the village of Maariyah, located outside the UN-patrolled zone on the western edge of Syria’s southern Daraa province.

Residents told the Associated Press news agency that Israeli soldiers, who advanced about 1 kilometer into Maariyah, blocked local farmers from accessing their fields.
The following day, protesters gathered to demand the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Maariyah. In response, Israeli soldiers opened fire, wounding a young Syrian man in the leg, according to the SOHR.
Amid these tensions, UN chief Guterres stressed that “in the occupied Syrian Golan, there should be no military forces in the area of separation other than UN peacekeepers – period.”
He added in a post on X that “Syria’s sovereignty, territorial unity, and integrity must be fully restored, and all acts of aggression must come to an immediate end.”
However, Mason believes that, despite experiencing discrimination under Israel’s occupation, the indigenous people of the Golan have not endured the same violent repression as Palestinians in the West Bank and East Jerusalem.
He said that while the Druze and Christian communities in the Golan Heights are “subject to discriminatory treatment compared to Jewish settlers,” they “have not yet faced the sustained level of systematic human rights abuses and violent repression suffered by Palestinians in the West Bank.”





























