RIYADH: Saudi Arabia emerged as the top issuer in the Gulf Cooperation Council bond market during the first half of 2024, raising $37 billion through 44 issuances, according to recent data.
The Markaz GCC Bonds and Sukuk Market Report indicated that this figure marks a 12.5 percent increase from the same period last year, representing 49 percent of the total new supply of GCC bonds and sukuk.
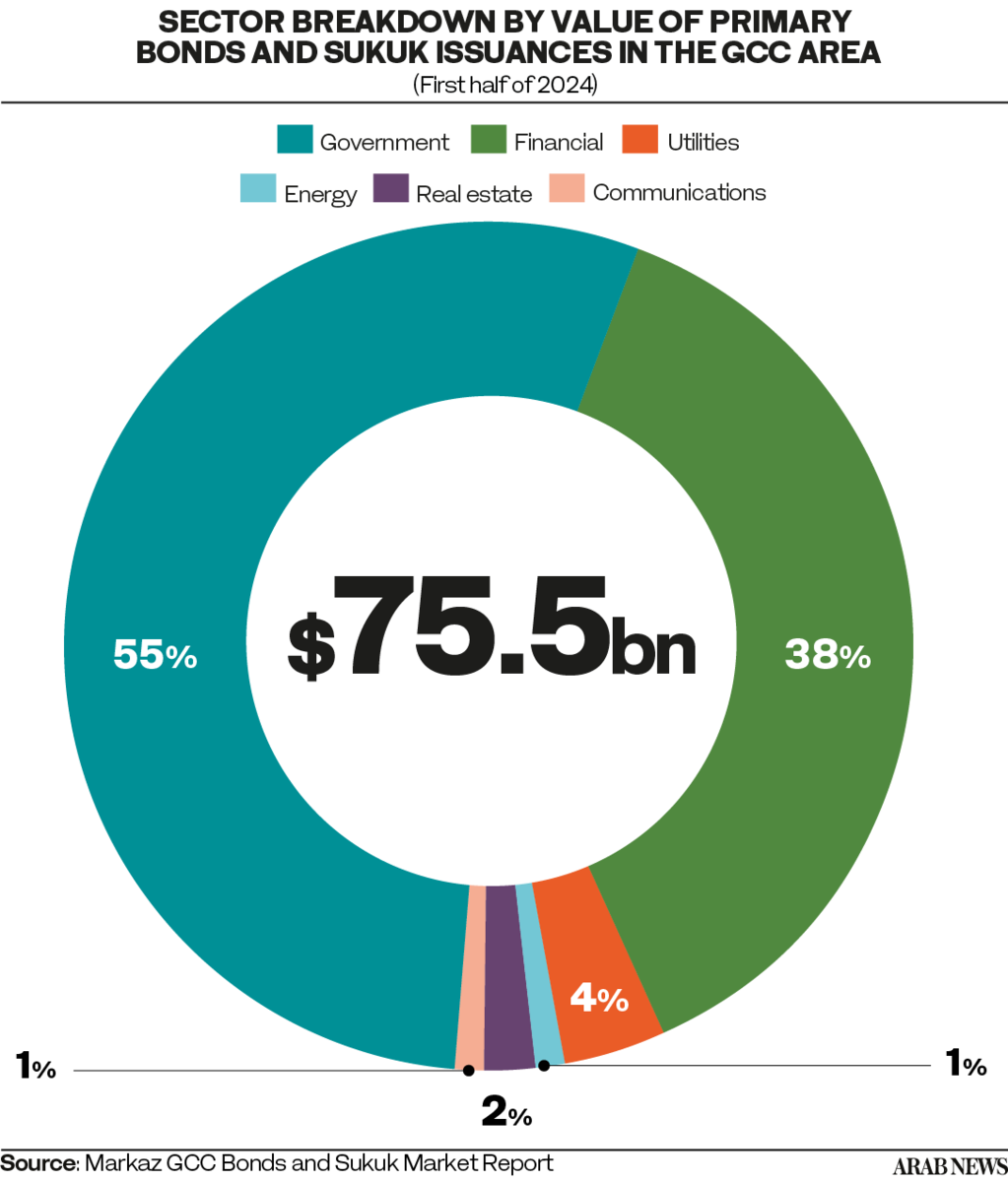
The overall value of GCC primary issuances reached $75.5 billion during this period, up 38 percent from $54.8 billion in the first half of 2023, with the number rising to 173 from 130.
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 includes several megaprojects that require substantial funding. While the Kingdom’s banks have traditionally relied on deposit growth as their primary funding source, the scale of these projects exceeds their liquidity capabilities.
Consequently, these banks are expected to seek additional deposits and access the international debt market to meet their financing needs. Additionally, these projects receive significant support from the central government and related entities.
The Public Investment Fund has announced plans to deploy $70 billion annually after 2025 and is considering its own fundraising initiatives.
Samer Jumean, partner and head of infrastructure at KPMG in Saudi Arabia, said in a Bloomberg interview an immense scale of financing is required, noting that while liquidity remains available, accessing capital markets is prudent.
Despite these ambitious funding needs, Saudi banks’ balance sheets are still considered healthy, with S&P Global Ratings assigning investment-grade ratings and stable outlooks to most key lenders. They may not be able to shoulder the entire financial burden of Vision 2030 on their own, however.
Debt issuances by geography
According to the Markaz report, the UAE followed Saudi Arabia in terms of value, raising $20.6 billion through 65 issuances during the first half of 2024, compared to $15.4 billion from 58 issuances during the same period last year. This represented 27 percent of the total value of primary GCC bonds and sukuk issuances.
Qatari entities were the third-largest issuers within the GCC, with $10.5 billion, marking a 416 percent increase from the same period last year.
Bahraini institutions raised $3 billion through 4 issuances, capturing 4 percent of the market while Omani entities secured $1.7 billion, representing 2 percent of the total.
Kuwaiti issuers raised $2.6 billion through 15 offerings, a 791 percent increase from $300 million in the same period last year, also representing 4 percent of the market.
According to the report, 75 percent of GCC conventional and sukuk bond offerings in the first half of 2024 were rated by major credit rating agencies, including S&P, Moody’s, Fitch, and Capital Intelligence.
This is a decrease from 85 percent in the same period the previous year. Of these rated issuances, 71 percent were classified as investment grade, highlighting a strong focus on high-quality debt despite the overall decline in the proportion of rated bonds.
This shift indicates evolving dynamics in the regional bond market, with a slightly reduced emphasis on credit ratings but a sustained preference for investment-grade securities.
Sector allocation
According to Markaz, the government sector led primary debt offerings by value in the first six months of this year, raising $41.5 billion, or 55 percent of the total GCC issuances.
In July, Saudi Arabia expanded access to its local bond markets by appointing five new financial institutions — Albilad Investment Co., AlJazira Capital Co., Al Rajhi Capital Co., Derayah Financial Co., and Saudi Fransi Capital Co. — as primary distributors of government debt instruments.
These institutions join existing primary dealers including Saudi National Bank, Saudi Awwal Bank, and AlJazira Bank, as well as Alinma Bank, and AlRajhi Bank. This expansion aims to diversify the investor base and enhance opportunities for participation in the local debt market through additional distribution channels.
Following the government sector, the financial segment, including quasi-government entities, raised $28.8 billion, or 38 percent of the total offerings. The utilities sector came next, raising $2.9 billion through five issuances, representing 4 percent of the market.
Sovereign versus corporate
The Markaz bonds report highlighted a notable shift toward sovereign debt issuance in the GCC for 2024. Total primary sovereign issuances surged 77 percent to $41.5 billion in the first half of the year, compared to $23.4 billion in the same period of 2023.
Saudi Arabia led this increase with a $5 billion sukuk issuance, marking the largest sovereign issuance in the GCC. In contrast, Kuwait did not participate in sovereign bond issuance during this period.
Corporate debt issuance in the GCC also saw growth, rising 8 percent to $34 billion in the first half of 2024, up from $31.4 billion the previous year. Government-related entities accounted for $9.1 billion, or 22 percent of the total corporate debt issued.
The UAE emerged as the top issuer with $12.8 billion in corporate debt, while Saudi Arabia’s PIF made headlines with its $1.8 billion issuance, the largest corporate bond offering in the GCC during this period.
Conventional versus sukuk
In the first six months of 2024, Saudi Arabia led the regional sukuk market with a $5 billion issuance, significantly contributing to the overall rise in sukuk across the GCC.
Sukuk volumes increased 14 percent compared to the same period in 2023, totaling $26.6 billion through 31 issuances.
In contrast, conventional bond issuances surged to $48.8 billion, marking a 56 percent rise from the first half of 2023, with the Saudi government also leading in this category with a $4.8 billion offering.
S&P Global Ratings projects a stable global sukuk issuance forecast of $160 billion to $170 billion for the year, reflecting strong early performance in 2024.
Global sukuk issuance reached $91.9 billion in the first six months, up slightly from $91.3 billion the previous year. Notably, foreign currency sukuk saw a 23.8 percent rise, reaching $32.7 billion, driven primarily by issuers from Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Oman, as well as Malaysia, and Kuwait.
























