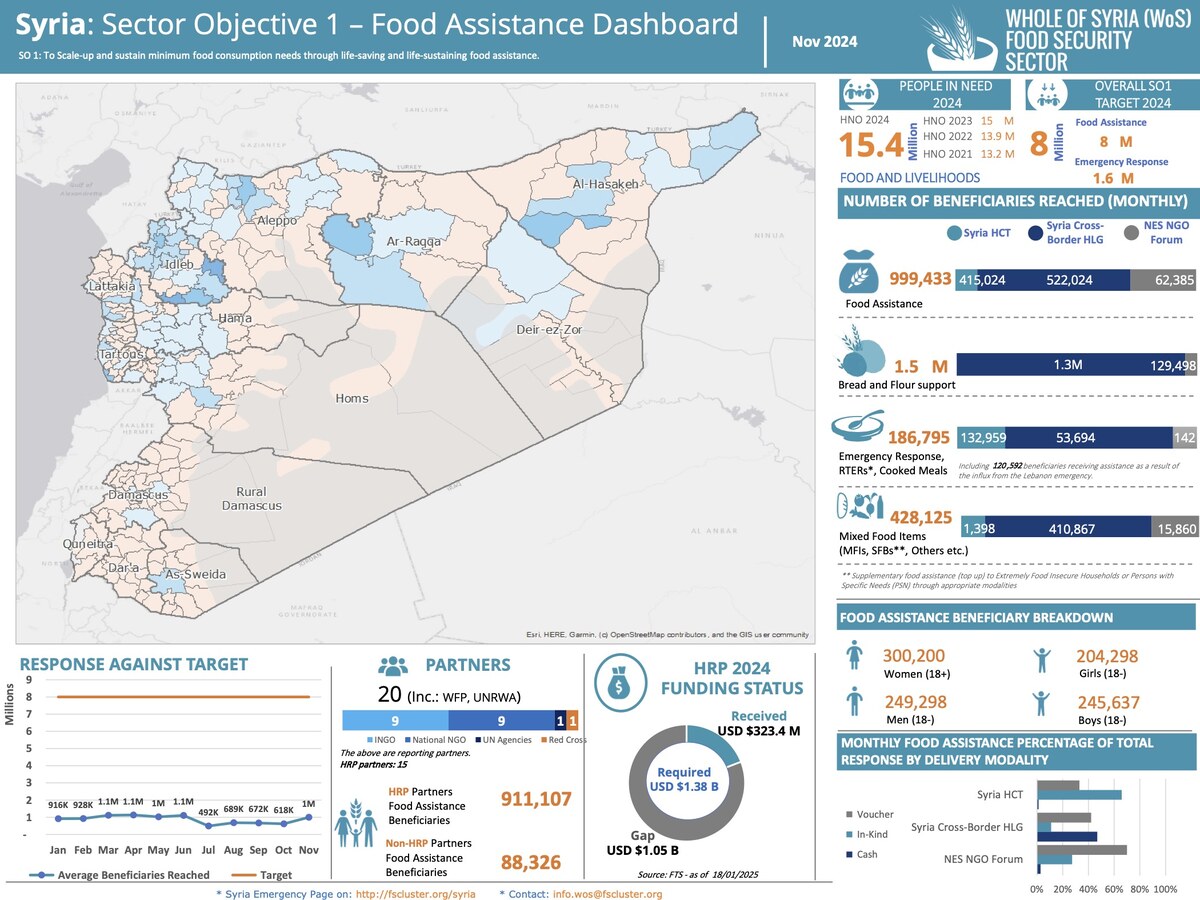
NEW YORK CITY: Four doctors from the US, UK and France, who have been working with teams in Gaza to support its healthcare system, have described witnessing “appalling atrocities” under Israel’s military offensive.
The four specialists told an event at the UN headquarters this week that doctors in the enclave are faced with “horrific decisions” almost every day as a result of the war.
Nick Maynard, a cancer surgeon from the UK city of Oxford, has for the best part of the past 15 years been traveling to the Gaza Strip to teach, carry out surgeries, and help develop local healthcare capacity.
Because of his long association with Gaza, Maynard thought he was prepared for what awaited him when he again set foot in the Palestinian territory last December as part of the first UK emergency medical team to arrive since the outbreak of war in October.
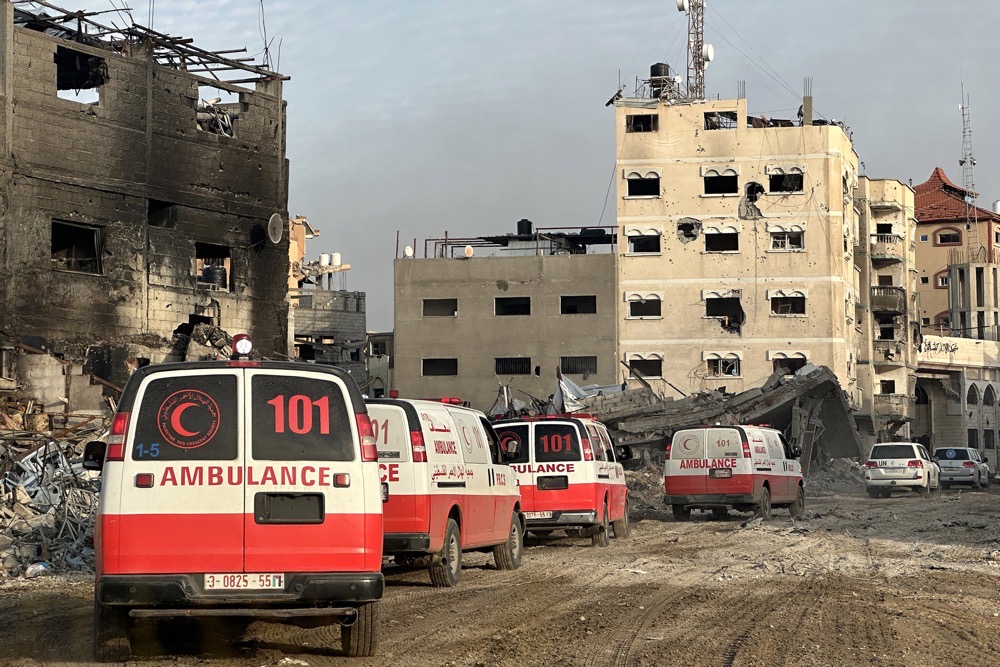

According to the World Health Organization, there have been 164 attacks on healthcare infrastructure in the Gaza Strip since Oct. 7. (AFP)
However, what he encountered during his two weeks at Al-Aqsa Hospital were “the most appalling atrocities,” he said. “I saw things that I never would have expected to have seen in any healthcare setting.”
The Israeli government says its military does not target civilians or hospitals, and blames Hamas for conducting military operations and launching rockets from crowded residential areas. Maynard rejects this claim.
Any medic who has worked in Gaza in recent months can dispel “with absolute certainty” the notion that Israel is conducting targeted bombing of Hamas militants and is protecting civilians,” he said.
“There is mass, indiscriminate bombing, killing many, many thousands of civilians, and a very clear targeting of healthcare facilities and workers, and deliberately destroying the infrastructure of all the hospitals to make it almost impossible to provide anything resembling normal healthcare to the population of Gaza.”
In fact, Maynard said Israel’s actions resemble the dictionary definition of genocide — designed to drive the Palestinian people out of Gaza.
“I spent some time looking at the definition of genocide in a variety of dictionaries,” he said. “And what is going on in Gaza fulfills every single definition of genocide that I have read.
“To those of us who’ve been on the ground there, and indeed, more importantly, all the Gazans I’ve spoken to, say the endgame of the Israeli government is to force them out completely from Gaza, to eradicate them from that land.”
Maynard was speaking at the UN headquarters in New York, where he was among a delegation of doctors meeting with UN representatives, who later met with Biden administration officials and members of Congress in Washington on Friday.
Their goal is to “instill a sense of urgency,” make sure US decision-makers and the international community “know what we know,” and hammer home that “the only way to prevent that ongoing humanitarian catastrophe is an immediate and permanent ceasefire.”
According to the World Health Organization, there have been 164 attacks on healthcare infrastructure in the Gaza Strip since Oct. 7, when the Hamas-led attack on southern Israel triggered Israel’s retaliation against the group’s Gaza stronghold.

More than 30,000 Palestinians have been killed in Gaza since the conflict began. (AFP)
The UN agency says more than 400 medical workers have been killed since the conflict began. Before the war there were 6,000 beds at 39 hospitals in Gaza. Now roughly 295 hospital beds remain.
Israel has accused Hamas of building a vast tunnel network under Gaza’s hospitals, which it claims contain command centers, weapons caches, and places for holding Israeli hostages taken during the Oct. 7 attack.
“I’ve paid many visits to Al-Shifa Hospital and a lot of the other hospitals as well and I’ve never, in any service, any time during my visits, seen any evidence of military activity of any Hamas militants in any of the hospitals,” said Maynard.
“The Israelis have provided no credible evidence whatsoever to support those claims.”
Also among the doctors’ delegation was Zaher Sahloul, a Syrian-American doctor who is co-founder and president of MedGlobal, an NGO that provides emergency response and health programs around the world.
Sahloul, who was in Gaza in January, said the enclave is reaching a “tipping point.”
“Gaza at this stage is unlivable because of the persistent destruction of the infrastructures that are required for life,” he said.
The continued squeeze on deliveries of humanitarian assistance and commercial goods is pushing the population to the brink of famine, particularly in northern Gaza, with malnutrition and food insecurity reaching “catastrophic levels,” said Sahloul.
INNUMBERS
• 164 Attacks on healthcare infrastructure in Gaza since Oct. 7.
• 400 Medical workers killed since eruption of conflict.
• 295 Hospital beds currently available in Gaza.
Source: WHO
Chronic conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and various cancers that require regular medication, dialysis, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, are going untreated as a result of shortages and the destruction of healthcare infrastructure, he added.
More than 30,000 Palestinians have been killed in Gaza since the conflict began, including 13,000 children, according to the local health ministry.
Sahloul believes this is “an underestimate of the real numbers,” however, as roughly 5,000 people are still thought to be buried under the rubble of collapsed buildings.
And these numbers “will continue to accelerate even if the war stops right now,” he said.
“The collapse of the healthcare system will lead to pregnant women dying from bleeding and diarrhea patients dying from dehydration.”

Zaher Sahloul, who was in Gaza in January, said the enclave is reaching a “tipping point.” (Supplied)
And if Israel follows through on its threat to mount an attack on Rafah, Sahloul fears such an incursion will result in a “bloodbath,” and the death of an estimated 250,000 people.
During his address to UN officials, Sahloul showed a photograph of Hiam Abu Khodr, a Palestinian child who lost her father and brother when a bomb destroyed her home. Her mother was also injured in the blast. Hiam, meanwhile, suffered third-degree burns to 40 percent of her body.
“If you want to define post-traumatic stress disorder, this is what it looks like in the face of a child who is 7 years old,” said Sahloul.
Hiam waited weeks for an evacuation to Egypt for treatment. However, she died of her injuries two days after leaving Gaza. According to Sahloul, just 10 percent of the 8,000 patients in need of evacuation for treatment abroad have been able to leave.
Sahloul described “apocalyptic” scenes in the few hospitals that remain partially functional in Gaza, where the wounded brought into overcrowded wards are mostly treated on the floor. He described the case of 12-year-old Mohmad Abu Shahla, who arrived unable to breathe.

Any medic who has worked in Gaza in recent months can dispel “with absolute certainty” the notion that Israel is conducting targeted bombing of Hamas militants and is protecting civilians,” said Nick Maynard. (AFP)
Mohmad had surgery to remove shrapnel from his abdomen before he was whisked to the intensive care unit where Sahloul tended to him. However, the boy “never woke up.”
“We were not able to communicate with his family. We sent him to the morgue. And I made a copy of his death certificate, to keep it as a proof.”
On Thursday, displaced civilians camped out in the grounds of Al-Shifa Hospital in northern Gaza were ordered to leave immediately as Israeli forces continued their raid on the hospital complex.
Scores of people have reportedly been killed and 70 health workers arrested during the raid, with thousands more civilians sent south to Rafah, where some 1.4 million people were already hemmed before recent attacks on Khan Younes.
While many “incredibly heroic” healthcare workers decided to stay, Thaer Ahmad, a Palestinian-American emergency medicine physician who was with Sahloul in Gaza in January and who also spoke at the UN event, chose to evacuate before the raid.
On his way into Gaza, Ahmad said he saw “hundreds of trucks” lined up on the Egyptian side of the border waiting to bring aid into the enclave.

The Israeli government says its military does not target civilians or hospitals. (AFP)
“We know that these trucks have baby formula. We know that they have many needed items,” including diapers, inhalers, and sedatives for pain relief, he said.
“This is something that we could be using for our patients who are in pain as we’re trying to reset their fractures, clean their burns. It’s an incredibly painful process and this is something that can help. We’re not able to get this into the Gaza Strip because the trucks are stalled.
“Or if someone is having difficulty breathing as you may suspect may happen as bombs are dropping, and air fills with smoke, we’re not able to get a rescue inhaler to be able to treat their asthma.
“Or diapers for families. We’ve heard of people having to use plastic bags because they cannot find diapers and if they do find them, the price is incredibly high because of inflation and the lack of supplies.
“I hope that this can bring home the urgency that exists on the ground. We need our hospitals to be able to stand. We need the bombs to stop dropping, hopefully through a ceasefire. And we hope that we can get the necessary items in to help alleviate the incredible amount of suffering that’s taking place in the Gaza Strip.”
Also among the doctors’ delegation was Amber Alayyan, a pediatrician from Texas, who has been working with Medecins Sans Frontieres for 13 years.
As a result of the scarcity of medicines, Alayyan said, doctors are faced with “horrific decisions,” sometimes having to intubate patients without anesthetics.
Displaced people with nowhere to go are sheltering in hospitals and sleeping on beds intended for patients, she said.
“What does that mean for injured people? They arrive, they get a quick and dirty surgery in an emergency room or in an operating theater, and they have nowhere to be hospitalized afterward.
“Or when they are, they’re lost in the hospital and our teams spend all day searching for the patients they just operated on 12 hours before.
“The longer the war goes on, the longer these wounds have to rot. I mean really rot. No hospital in the world — high-income, low-income — could cope with the amount of injuries that we’re seeing and the needs that we’re seeing on the ground.”
The collapse of Gaza’s health system and shortages of food have left pregnant and lactating women and their newborns especially vulnerable, said Alayyan.
These women “were already facing high iron deficiency, anemia, before the war, which put them at risk for hemorrhage during birth,” she said.

“All the Gazans I’ve spoken to, say the endgame of the Israeli government is to force them out completely from Gaza, to eradicate them from that land,” Nick Maynard. (AFP)
“With the war, it puts them in a state of undernourishment and potentially malnutrition, which means that they can’t breastfeed their children properly. The milk doesn’t necessarily come in and it’s definitely not enough.
“The other population is children under 2 years, which is the breastfeeding age. Those children need to be breastfed. If they can’t, then they need a formula. To have formula you need clean water. None of these things are possible.”
She said women are “squeezing fruit dates into handkerchiefs and drip feeding their children with some sort of sugary substance to nourish them.”
“How many people are going to need prosthetics? What is the socioeconomic status of Gaza going to look like in five years? In three years? In three months? How can this population, that is so incredibly resilient, rebuild itself? And the longer the war goes on, the harder this becomes.”
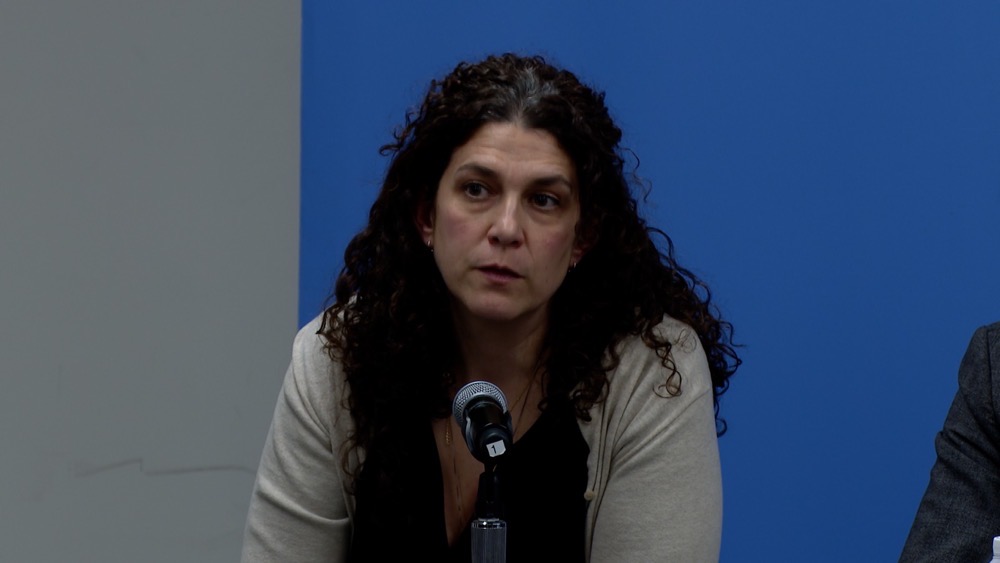

“No hospital in the world — high-income, low-income — could cope with the amount of injuries that we’re seeing,” said Amber Alayyan.
Ahmad said he has often heard it said in Gaza that “there is a war after the war.”
“And it’s a day of reckoning for the people, to think about everything that they’ve lost, all of the struggles that they’ve been through.”
He added: “Oftentimes, what we can see is there can be a paralysis by analysis. And there could be a lot of deliberations that take place.
“We just want to impress upon the people who are at the table that this is very urgent and we need things to change within the next few hours or days, not weeks.”