NEW YORK CITY: With hostilities between Israel and the Iran-backed Hezbollah militia on the brink of all-out war, the UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres told Arab News in an exclusive interview on Friday that the world cannot allow Lebanon to become another Gaza.
The pager and walkie-talkie attacks across Lebanon last week, which left 37 dead and more than 3,000 injured, and which were followed by further exchanges of fire across the Lebanese border, have raised regional tensions to breaking point.
A doctor performs an eye surgery at a hospital in Beirut on a man who was injured by a communication device blast. (AFP)
Guterres said an all-out war between Israel and Hezbollah “is something we need to avoid at all costs.” Yet, against this backdrop, he says there is “a growing conscience that we must stop. We must stop this war in general. We must stop the war in Gaza.”
Speaking to Arab News ahead of the high-level week of the UN’s 79th General Assembly, which takes place as the war in Gaza nears its grim one-year anniversary, Guterres acknowledged the conflict has exceeded his expectations in terms of its duration and the “unprecedented level of destruction and suffering.”
As he reiterated his “vigorous” condemnation of the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, he again stressed “that can never justify the collective punishment of the Palestinian people.”
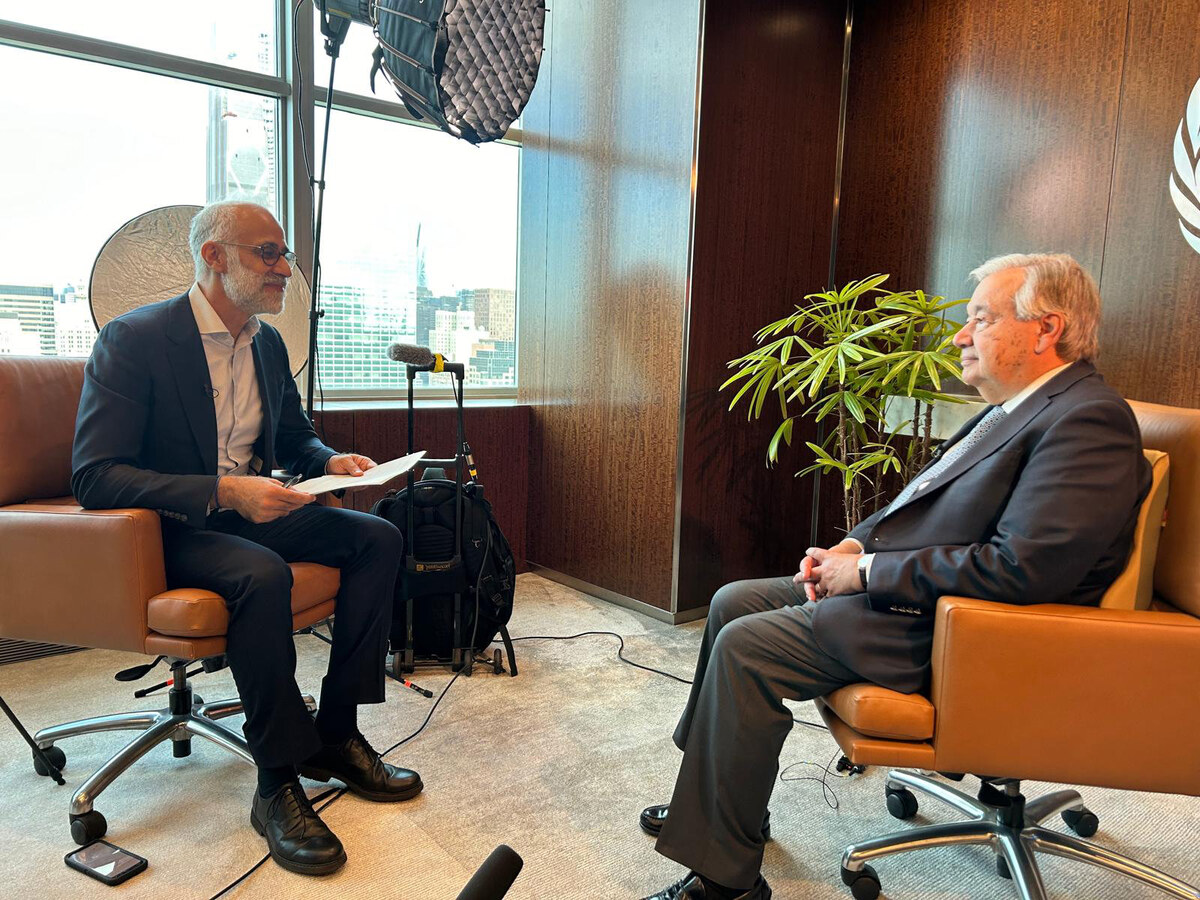

UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres speaks to Ephrem Kossaify of Arab News. (AN photo)
When asked about the UN’s responsibility for the failure to end the war, Guterres made it clear that the responsibility lies with those who initiated the conflict.
He said the UN has consistently called for ceasefires and humanitarian assistance from the beginning of the hostilities, but added “it’s impossible to convince those who do not want to be convinced.”
Guterres said he was saddened at not being able to do more for the people of Gaza, and attributed this to security concerns and restrictions imposed by Israeli authorities in the war ravaged enclave.
Calling for a two-state solution to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, he said: “There is no humanitarian solution for humanitarian problems. The solution is always political. That is why we need to stop the war.”
Guterres also addressed the limitations of the UN’s power, noting that while it is a strong voice for peace and adherence to international law, its effectiveness is often hindered by geopolitical dynamics, particularly within the Security Council.
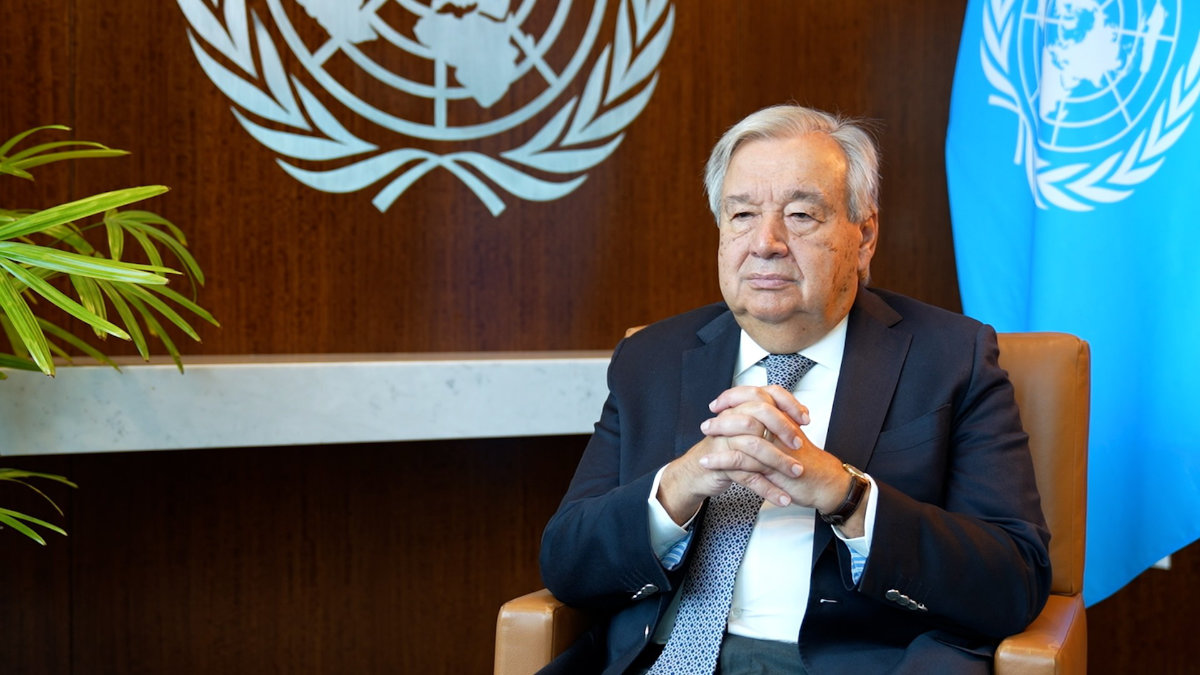

UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said a political solution is the only viable solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. (AN photo)
Calling on the US to stop supplying weapons to Israel, meanwhile, is an exercise in futility, he said. “I simply know that that would not happen. It’s not worth concentrating efforts where the results are impossible.”
He was unequivocal, however, on the need to implement all the deliberation of the International Court of Justice, which in January ruled there was a risk that genocide is being committed in Gaza.
Asked whether he is in favor of issuing arrest warrants for Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, Guterres said he supports “all the decisions of the ICC.”
Q. Mr. Secretary-General, let’s start with Lebanon. The latest pager attacks in Lebanon have left so far 37 killed and over 3,000 injured. Is this another example of total disregard for the civilian toll? And is this the new norm now in the Middle East conflicts?
A. It is a very serious escalation. But I think that even more important than the fact that you mentioned is the idea which we now know, that this was triggered now because there was a suspicion that they were being discovered. And so, as they were being discovered, they were made to explode, which means that the objective was not to explode them now. And this kind of devices, this kind of operation, makes sense as a pre-emptive strike before a major military operation. So, even more worrying than the events themselves is the fact that they show that there is a serious risk of an all-out war in Lebanon, and that is something we need to avoid at all costs. We cannot allow Lebanon to become another Gaza.
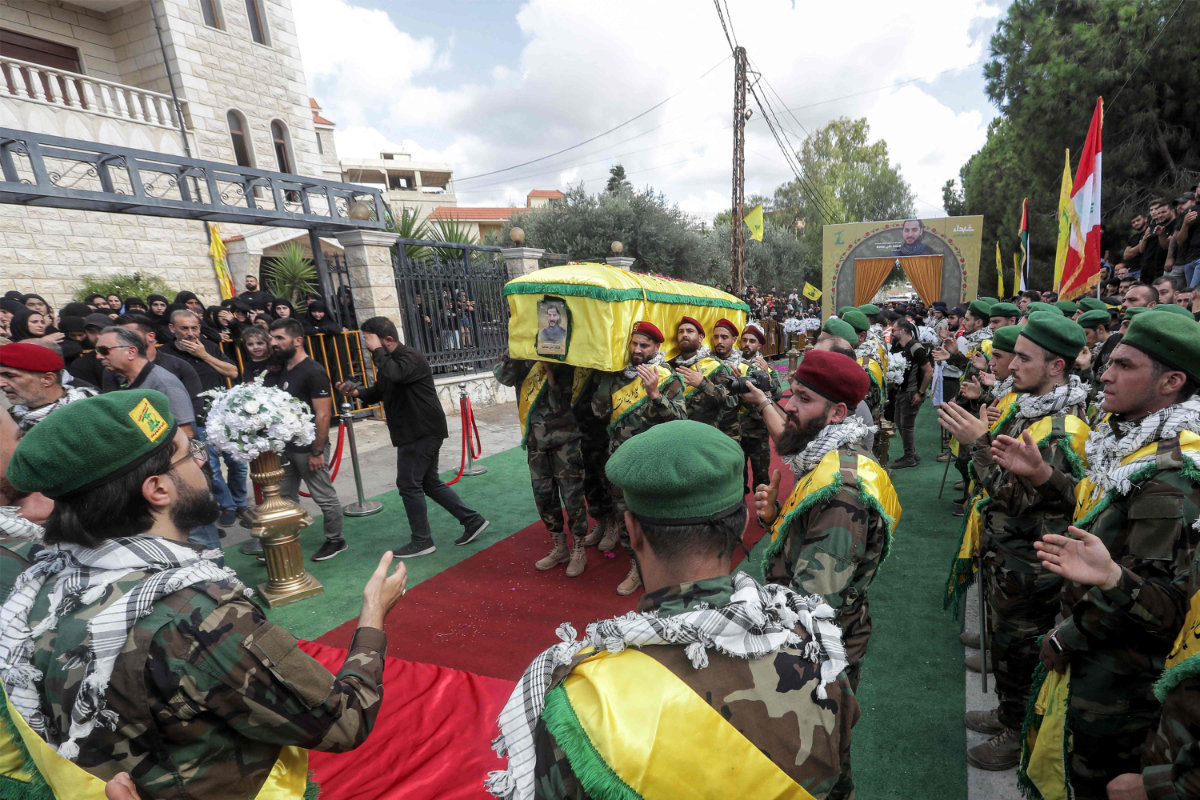

Hezbollah members carry the coffin of a comrade — a victim of Israel's pager attack — during a funeral in Adloun south of Tyre in southern Lebanon. (AFP)
Q. Are you in touch with Israel and Hezbollah? What are you hearing? Is an all-out escalation non-avoidable at this stage? And is there anything the UN can do?
A. At the present moment, we are witnessing an escalation, both a physical and a verbal escalation, but there is also a growing conscience that we must stop. We must stop this war in general. We must stop the war in Gaza. We must stop. And that it is absolutely essential to first start de-escalating, and second, to have a serious negotiation to solve once and for all the problems of demarcation on the Blue Line and to stabilize the relationship there without more casualties, especially without more civilian casualties.
Q. For almost a year now, the world has been watching some of the most traumatizing images of death and blood in Gaza. The longest and most atrocious war between Israelis and Palestinians. Did you expect this to take this long? And do you see an end in sight?
A. Sincerely, I didn’t expect it to last. And since the beginning, I’ve been asking for a ceasefire, humanitarian ceasefire, since the very beginning. I condemned vigorously the horrible terror attacks that were made on October 7 (last year) by Hamas, but that can never justify the collective punishment of the Palestinian people. And what we have seen in the last almost one year, was a level of death and destruction that is unprecedented in my period as secretary-general. And as you know, on top of all civilian death, we have had almost 200 of our own staff, humanitarian staff, killed. And this is something that obviously, in any circumstance, would need a serious investigation.
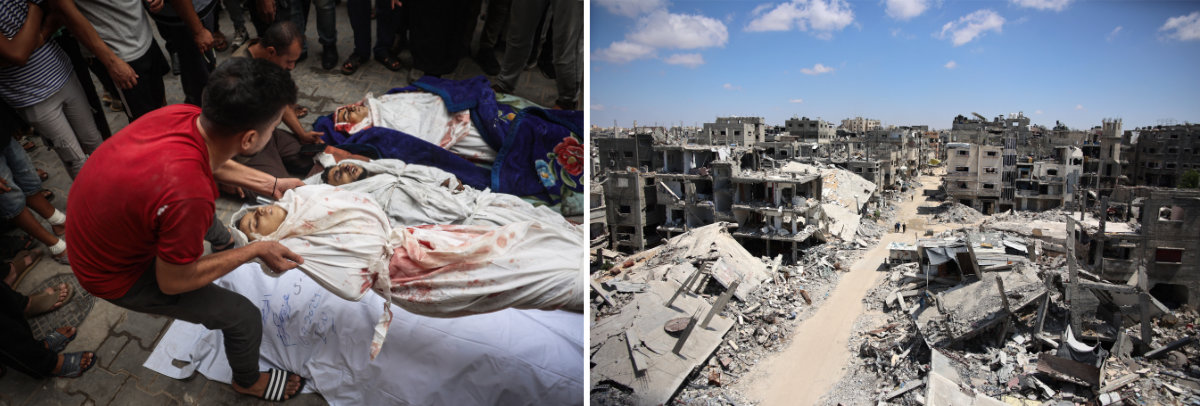

Almost a year after Israel launched its war of revenge against the deadly Oct. 7, 2023 attack by Hamas militants, Gaza has been almost totally destroyed and more than 41,000 people killed. (AFP photos)
Q. Do you or the UN take a personal responsibility for the failure to end the war?
A. Let’s be clear: The responsibility for the war is of those that make the war. Normally, this kind of question is asked to divert the attention from who is causing the problem. Could the UN have done more? I sincerely never felt that we had an opportunity to really do more than what we have done from the very beginning. And from the very beginning, we have asked for ceasefire, for release of hostages, for effective humanitarian aid. Since the very beginning, our voice has been loud and clear. From the very beginning, we have put pressure on all, namely, on countries that could have a direct influence on Israel. But let’s be clear: It’s impossible to convince those that do not want to be convinced.
Q. I was reading that during the Cambodian genocide, critics of the UN used to say, “Oh, look at the UN. They are distributing sandwiches at the gates of Auschwitz. And it got me thinking about Gaza today, where the UN is not even able to do that: distribute sandwiches in Gaza. Now, everyone who knows you describes you above everything else as a humanitarian. As a humanitarian, how do you feel about the fact that you haven’t been able to get food and medicine into Gaza?
A. Well, there has been consistently a series of obstacles, obstacles caused in many aspects, directly by the Israeli authorities, obstacles caused by the insecurity in the area, by the fact that law and order has completely broken in this dramatic situation. And you can imagine how deeply saddened I am not to be able to do much more. And the proof that we are not doing more because of the obstacles created to us is the vaccination of polio. When those obstacles disappear, humanitarian action becomes possible.
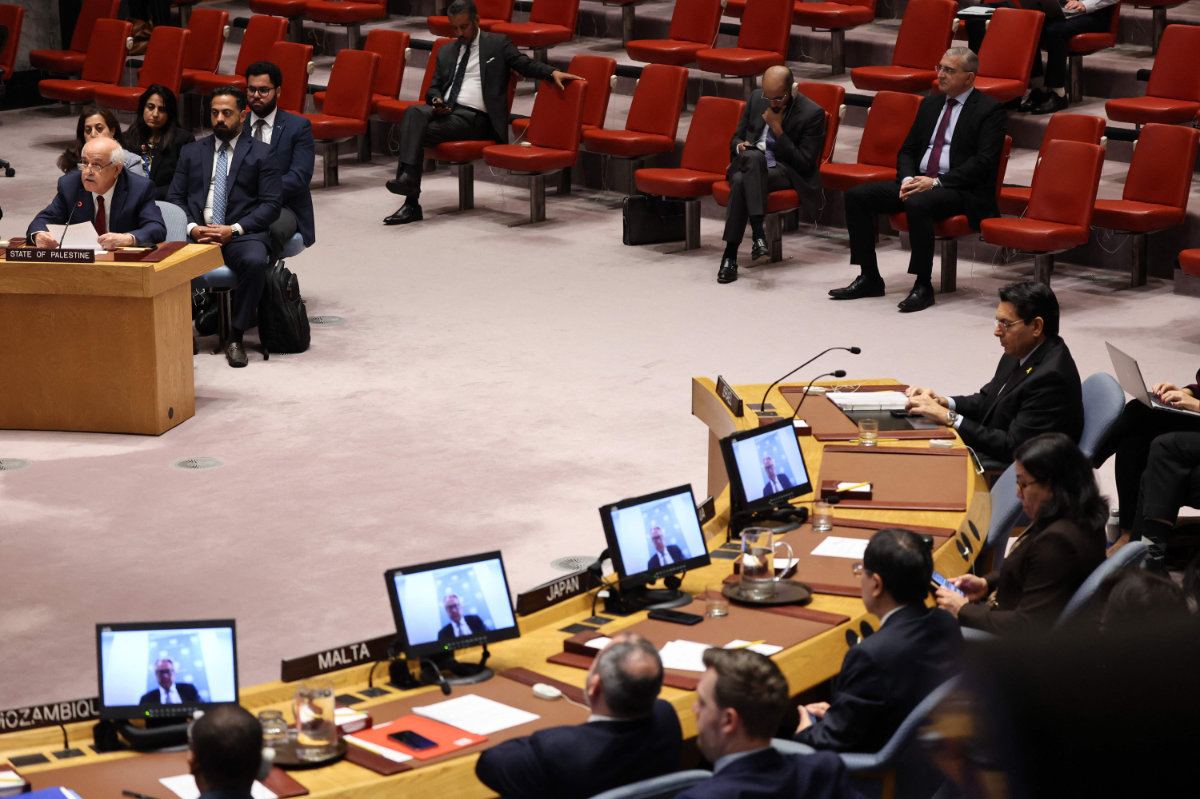

Members of the UN Security Council listen as Riyad Mansour, Palestinian Ambassador to the UN, speaks on the situation in the Middle East. (Getty Images/AFP)
So, it’s not that UN is not able to do more. It’s not that the other agencies are not able to do more. It is that until now, we have not been allowed to do more. When we are allowed, we do and we deliver, as it was demonstrated. But once again, I was for 10 years the High Commissioner for Refugees, and I always said there is no humanitarian solution for humanitarian problems. The solution is always political.
That is why we need to stop the war. That is why we need to create a clear road map for a two-state solution, a two-state solution in line with all the deliberations that the international community has already taken allowing Israelis and Palestinians to live together in peace and security.
Q. I can’t help but notice that you have avoided calling directly on the US to stop supplying arms to Israel, and you said many times that you prefer to focus on things that are more achievable.
A. No, I simply know that that would not happen. I was very clear: I think I should concentrate my efforts on what can produce results. It’s not worth concentrating efforts where the results are impossible.
Q. But given that 50,000 bombs have already been dropped on Gaza, and the ICJ has ruled that there’s a risk of genocide in Gaza, has your view on conditioning aid to Israel changed at all?
A. My view is that all the deliberations of the ICJ should be fully taken into account and fully implemented.
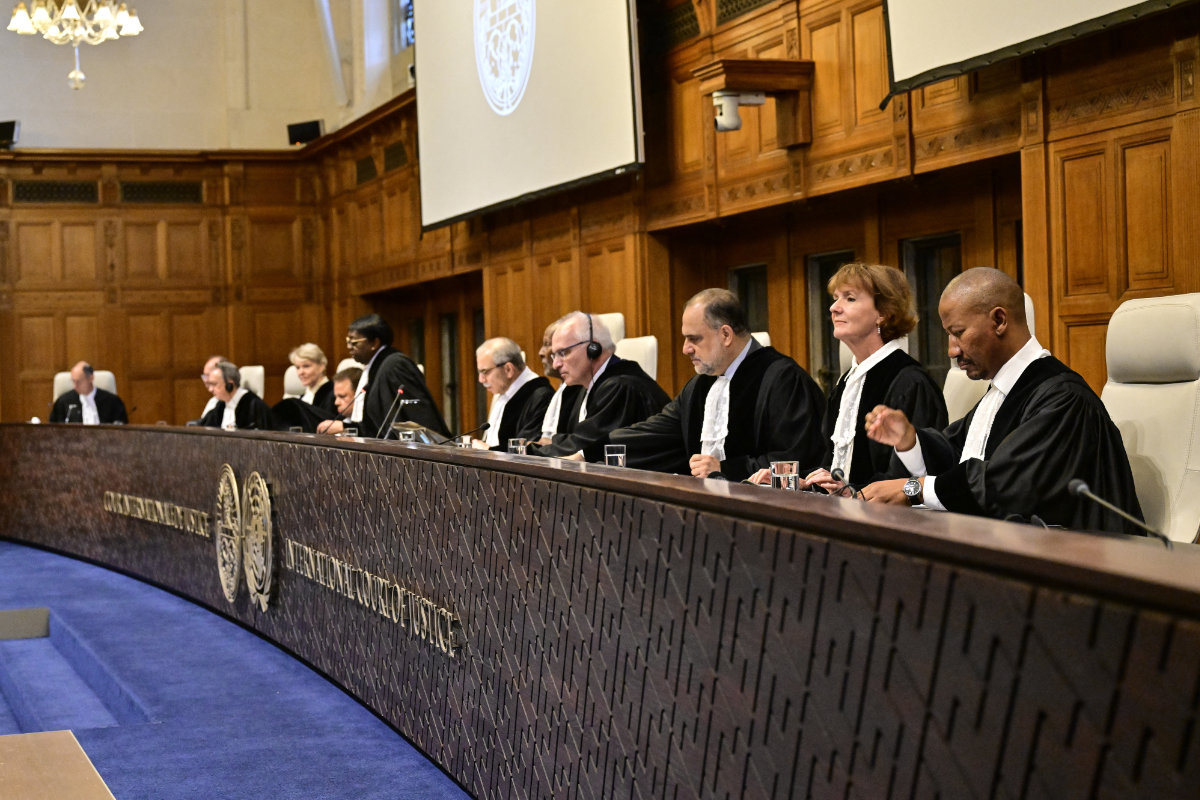

Magistrates are seen at the International Court of Justice as part of South Africa's request on a Gaza ceasefire in The Hague. (AFP)
Q. Many across the region and the world have a sense today that the UN has failed the Gaza test, and that fear has pushed this organization to retreat from international law itself, to self-undermine its own credibility as this war goes on unchecked. What is your answer to those, and do you agree that there is fear in this building to confront the US, to confront Israel?
A. There is no fear in this building to confront anybody. If I can be proud of anything, it is that my voice has been loud and clear in defense of the (UN) Charter, in defense of international law, in defense of international humanitarian law, and in defense of the right of self-determination of peoples, and in particular of the Palestinian people.
So, I don’t think the UN can be accused of not being very clear in all these aspects, as we have been clear in Ukraine and as we have been clear in many other situations around the world. We have no real power, let’s be honest. The body of the UN that has some power is the Security Council, and you know Security Council is paralyzed.
We have limited resources, but even without power and money, there are two things we have. One is a voice that nobody will shut up, and the second is the capacity to do our best to convene those with goodwill to put pressure on those that are responsible for the dramatic wars that we are witnessing, to make sure that those wars find their end as soon as possible.
Q. Do you support arrest warrants for Hamas political chief Yahya Sinwar and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu?
A. I support all the decisions of the ICC.

Israel's UN Ambassador Gilad Erdan raises image of Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar during UN General Assembly special session while Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu is depicted as Hitler during Australia demonstration. (AFP photos)
Q. You are the UN chief, so obviously you don’t use the word “genocide” lightly. And I am well aware that the concept of genocide has often been subject to political abuse. But for months now, we have been hearing every genocide scholar, international human rights lawyer, warning against the genocidal nature of this war. In Gaza, homes, schools. churches, mosques, universities, water and electricity infrastructure, food systems, medical institutions have been all but wiped out. Disease, poisoning of the earth, sexual assault, torture and advanced weapons. Do you believe, months later, that Israeli actions leave any room for doubt that what is happening is genocide?
A. Our position has always been very clear: It’s not for the Secretariat of the UN to classify acts like these. We rely on the International Court of Justice, and we will abide by the decisions of the International Court of Justice in the moment in which the International Court of Justice is dealing with it. So, as the UN, we have our court, and as the UN, we need to support in all circumstances the decisions of our court and not to replace it.
Q. Through the genocides of the past century, the Tutsis, the Bosnians, the Yazidi and the Rohingya, it was always afterwards that it became clear that the international community had failed in its duty to prevent mass atrocities, and ensure accountability for the perpetrators. Today, many are saying that the mandate of the UN genocide prevention office is more needed than ever. Why has your undersecretary, Alice Wairimu Nderitu, who was very vocal on Sudan and Armenia, to name two, been silent on Gaza?
A. She has not been silent. She has been active on Gaza and many other situations. It’s not for her to declare what is a genocide or not. She is our envoy on the prevention of genocide, and I am very proud of the work that she has been doing.
* * * * *
ANTONIO GUTERRES: DIPLOMAT WITH HUMANITARIAN BENT
Antonio Guterres, born on April 30, 1949, in Lisbon, Portugal, is the current secretary-general of the United Nations, a role he has held since January 1, 2017.
His career spans decades in politics, diplomacy, and international humanitarian work. Guterres graduated from the Instituto Superior Tecnico at the University of Lisbon in 1971, where he studied physics and engineering. He began his career as an assistant professor, specializing in systems theory and telecommunication signals before entering politics during Portugal’s post-revolution period in the mid-1970s.
Guterres’ early political career included being the head of the Secretary of State of Industry’s office and serving in the Portuguese parliament, where he chaired key committees on the economy, finance, territorial administration, and the environment. His international political involvement began in 1981 when he joined the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, focusing on migration, demography, and refugee issues.
From 1995 to 2002, Guterres served as the prime minister of Portugal, leading efforts to ensure minimum income guarantees and universal nursery schooling. His administration is also remembered for finalizing the transfer of Portuguese sovereignty over Macau to China in 1999. During this time, he championed UN intervention in East Timor, advocating for peace and independence in the region following years of conflict.
Internationally, Guterres became increasingly involved in refugee and humanitarian issues. In 2005, he was appointed as the UN High Commissioner for Refugees, where he expanded the organization’s emergency response capacity. His tenure was marked by his vocal advocacy for a humane approach to refugee crises, particularly in Iraq and Syria.
He also strengthened UNHCR’s presence in refugee host countries like Jordan and Lebanon. A notable achievement during this period was appointing US actress Angelina Jolie as a special envoy, a strategic move that raised global awareness about refugee issues.
Throughout his career, Guterres has been an advocate for diplomacy, sustainable development, and human rights. He remains a member of the Club of Madrid, an organization of former democratic leaders, and continues to push for global cooperation on pressing challenges such as climate change, conflict resolution, and migration.
He is married to Catarina Vaz Pinto, a former Portuguese deputy minister of culture, and has two children, a stepson, and three grandchildren.































