ATHENS: Taylor Swift fans were left disappointed earlier this month by news that the American pop star’s long-awaited tour dates in the Austrian capital, Vienna, were to be canceled owing to a terrorist threat to the concert venue by Daesh sympathizers.
On Aug. 7, Austrian authorities arrested three youths, aged 19, 17 and 15, who they claimed were involved in, or had knowledge of, a terrorist plot to attack the Ernst Happel Stadium where Swift was due to perform over the Aug. 8-10 period.
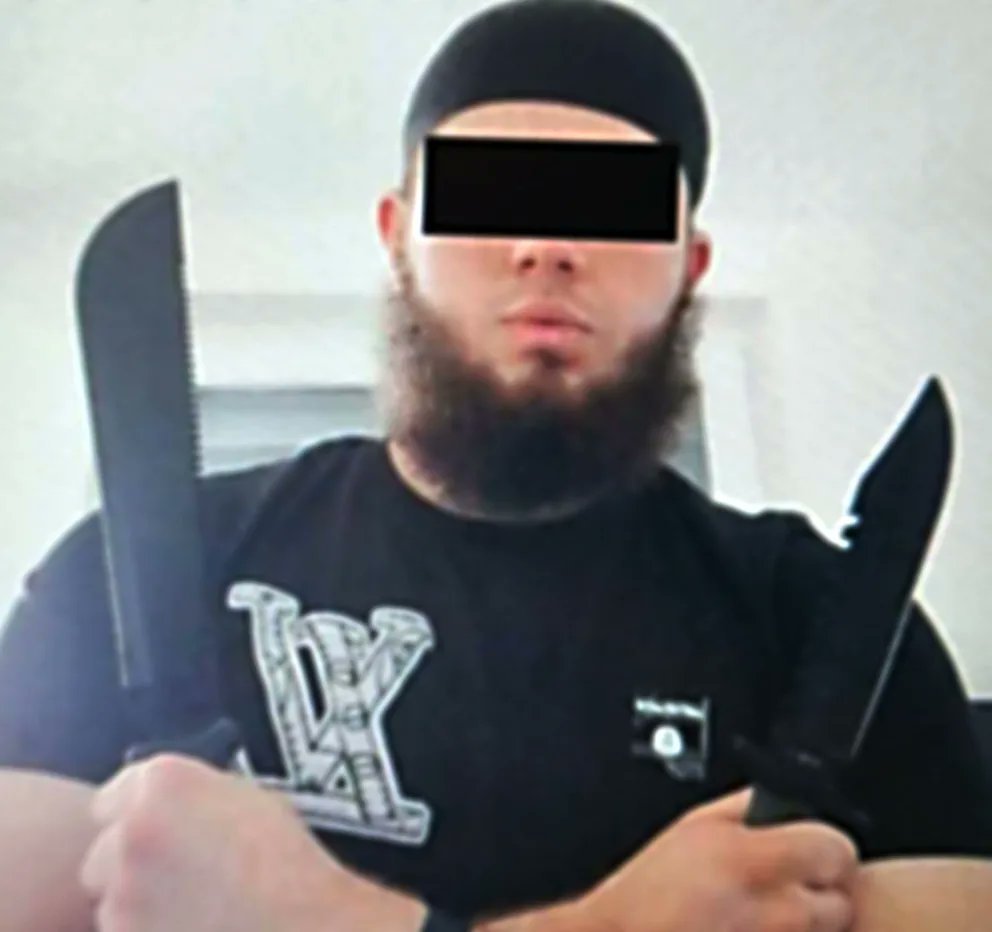

A closer view of the Austrian man of Macedonian descent, identified only as Beran A., who was arrested by Austrian police for allegedly plotting a terror attack on a stadium where American singer Taylor Swift was to hold a concert last week. (Social media photo
After searching the home of the 19-year-old suspect, an Austrian national with North Macedonian heritage, police found an array of edged weapons and bomb-making materials, counterfeit cash and Daesh propaganda.
Although the suspects had been taken into police custody, Swift’s promoter Barracuda Music decided to cancel the superstar’s three-date run of her Eras Tour, which was expected to attract 65,000 fans inside the stadium at each concert and 30,000 onlookers outside.
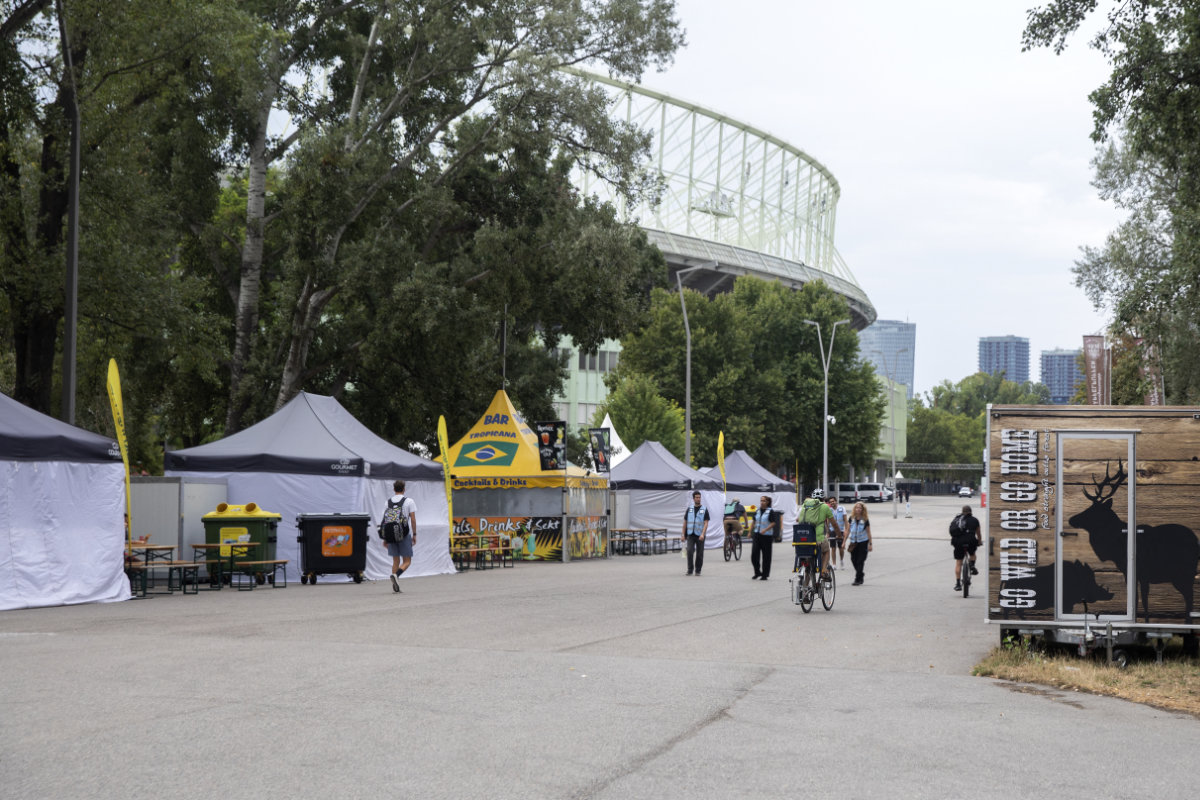

Merchandising booths for items related to US mega-star Taylor Swift are closed next to the Ernst-Happel Stadium in Vienna, Austrian, on August 8, 2024, after her three concerts were cancelled following after the arrest of a Daesh sympathiser in connection with an attack plot. (AFP)
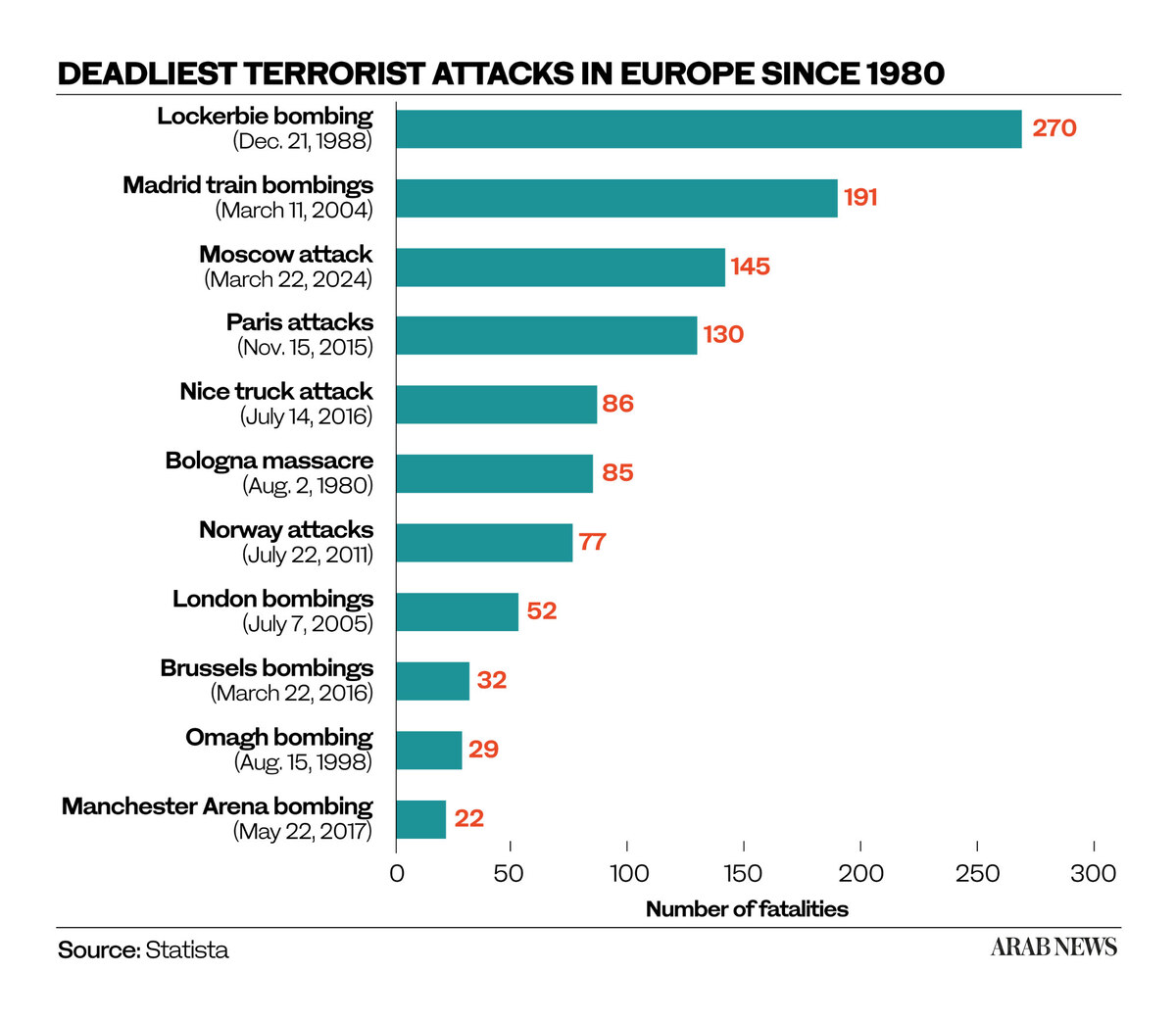
The decision was deemed prudent, especially given Daesh’s track record of attacking European concert venues. The group killed 90 at the Bataclan theater in Paris, France, in 2015. Two years later, a Daesh suicide bomber killed 22 at an Ariana Grande concert in Manchester, England.
Most recently, in March of this year, a massive, coordinated attack on Moscow’s Crocus City Hall by Daesh’s Central Asian branch, Islamic State in Khorasan, or IS-K, killed 145 people and injured more than 500.
What is surprising about the Vienna plot, however, is Daesh’s ability to continue recruiting followers in Western nations — long after its territorial defeat in Iraq and Syria in 2019 and despite international efforts to smash its leadership, financing networks and online presence.
“I’m not so surprised that there are still young people who join Daesh and want to do something in Europe,” Thomas Schmidinger, a Vienna-based political scientist and expert in extremism and deradicalization, told Arab News.
“I think the failure of Daesh as a state project in Iraq and Syria may have even increased the danger of terrorist attacks in Europe, because, in 2014 and 2015, people were going to Syria to join Daesh there. Now there is no more existing state project, but the organization continues to exist. The reasons why young people were attracted by this ideology are still here.”

An image grab taken from a propaganda video released on March 17, 2014 by the Daesh's al-Furqan Media shows the group's fighters driving on a street in the northern Syrian City of Homs. (AFP)
Schmidinger, however, believes it may have been a mistake to cancel Swift’s Vienna tour dates as doing so might encourage Daesh to threaten other such events in the future.
“The way the organizers of the concert reacted was actually a victory for the terrorists, because the Austrian police did catch the possible perpetrators and there was no reason to cancel the event,” he said. “This cancelation is now at least a propaganda victory for Daesh.”
Although authorities are desperate to avoid a repeat of the attacks in Paris, Manchester and Moscow, analysts say coordinated attacks of this scale are likely to be rare. Indeed, the majority of Daesh-inspired activities in the West, particularly in recent years, can be attributed to self-radicalized individuals acting of their own accord.
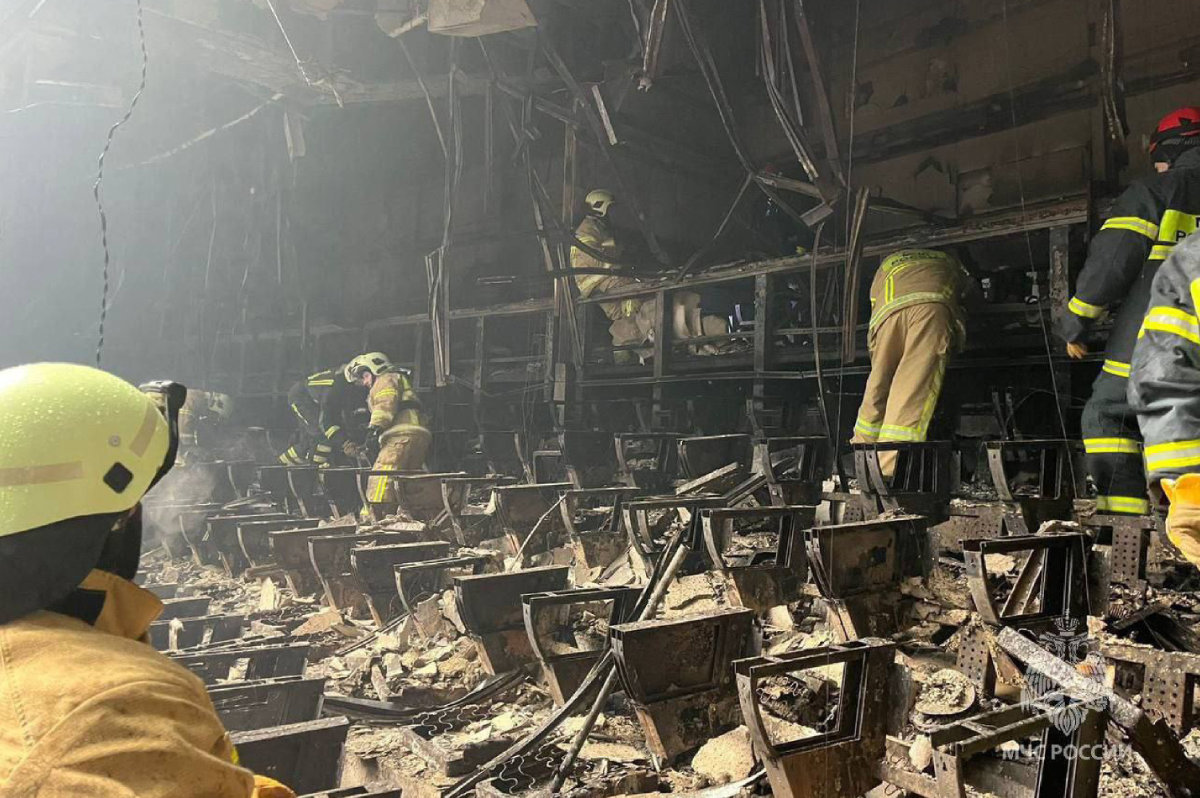

This handout photograph taken and released by Russian Emergency Ministry on March 23, 2024 shows
rescuers working inside the Crocus City Hall, a day after a gun attack in Krasnogorsk, outside Moscow. (Handout via AFP/File)
“You can tell the difference between someone who was inspired by Daesh, or just said they were Daesh, versus the ones who actually were Daesh,” Mia Bloom, professor of communication and Middle East studies at Georgia State University, told Arab News.
“There are degrees to which people claim Daesh affiliation and loyalty. They make this baya, or pledge of allegiance, to Daesh, but this doesn’t necessarily mean that Daesh has accepted it.
“For example, you can have people who are radicalized online who engage in a violent attack and they say they were inspired by watching beheading videos or propaganda that they’ve consumed.
“That’s very different from what we saw at the Bataclan in France, or in Charlie Hebdo, or in Dhaka, Bangladesh, where the perpetrators were trained in a Daesh camp. Daesh funded it, and Daesh live-streamed it on GoPro cameras.”
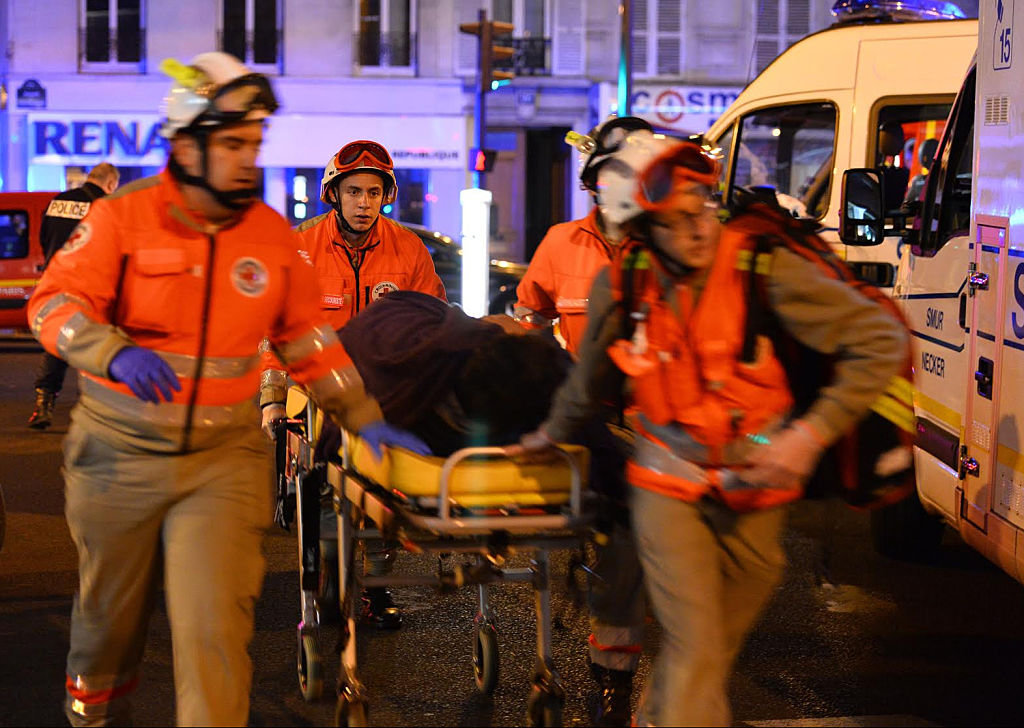

Rescuers carry a survivor of the Paris terrorist attack on the Bataclan theater on November 13, 2016. (Corbis via Getty Images/File)
Europe is not alone in facing an ongoing threat from Daesh. Although attacks in the US have been less common, the perpetrators of the 2015 shooting in San Bernardino, California, which left 16 dead, had pledged allegiance to Daesh on Facebook. A year later, a shooting at the Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Florida, claimed 49 lives.
However, there was no evidence that Daesh planned either attack.
“Daesh put out infographics on their successes from around 2014 to 2019,” said Bloom. “They put out a map of the US showing the attacks for which they were responsible, and they put Orlando in California and San Bernardino in Florida.
“If you don’t even know where the attack was, you probably weren’t responsible for it.”
INNUMBERS
• 28 Completed, failed or foiled terrorist attacks recorded in the EU in 2022.
• 380 People arrested by EU member states for terrorism-related offenses in 2022.
Source: Europol
Just last week, two Somali refugees living in Arizona pleaded guilty to attempting to join Daesh. The men, who were arrested in 2019, had allegedly made plans to travel to Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula, with one stating his wish to martyr himself and to become “the beheading guy.”
A June report by NBC highlighted the Department of Homeland Security’s identification of 400 Central Asian immigrants who may have been brought to the US by a Daesh-affiliated human smuggling network.
Though some of these individuals have been found, the department claims the whereabouts of at least 50 are still unknown.
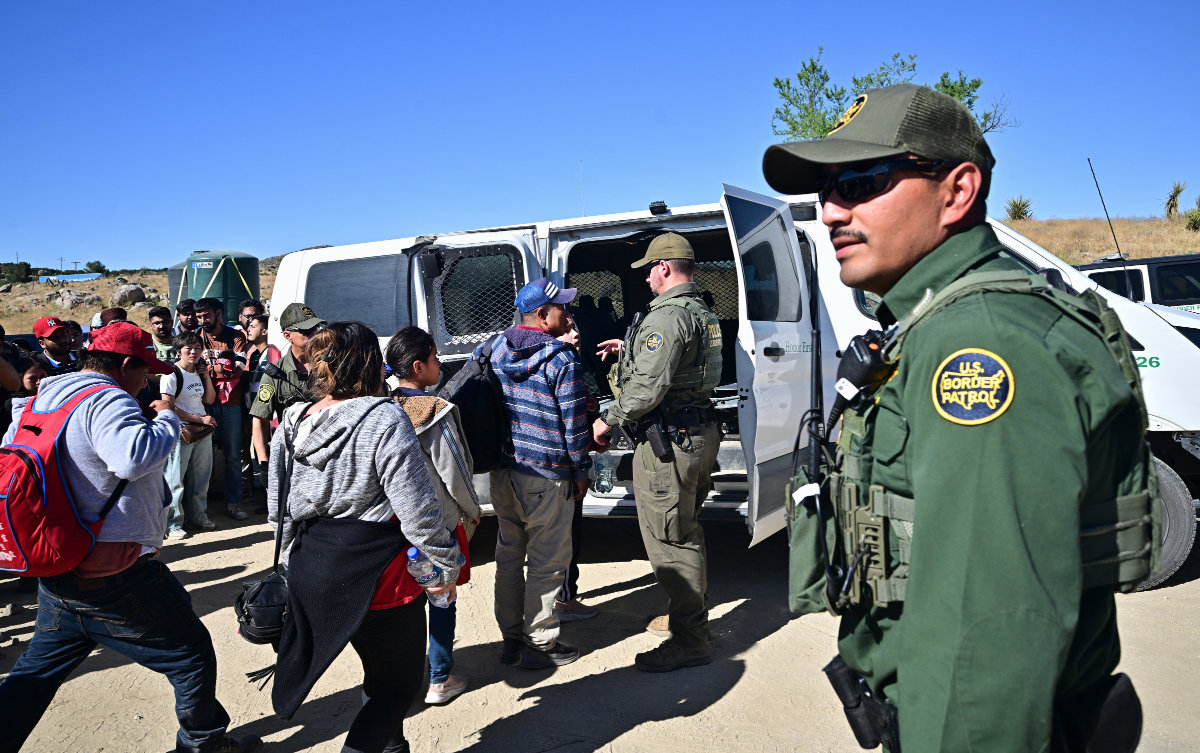

US Customs and Border Patrol agents load migrants into a vehicle after groups of migrants walked into the US from Mexico at Jacumba Hot Springs, California, on June 5, 2024. The Department of Homeland Security are on the lookout for possible Daesh terrorists being smuggled into the US. (AFP/File)
“Particularly through illegal immigration routes, that means most of the southern border, there has been an influx of people who have some degree of connection to Daesh,” Lorenzo Vidino, director of George Washington University’s Program on Extremism, told Arab News.
“This doesn’t mean that everybody smuggled in was Daesh, but nonetheless, the smuggling network had a Daesh connection, and so some individuals who have been arrested in the US have come through those routes and have known Daesh links.”
While Daesh may be able to infiltrate Western countries from overseas, Vidino says the number of native-born, self-radicalized individuals is likely to be far higher.
“If you look historically at the attacks that we’ve seen in the US over the last 10 years, most of them were perpetrated by Americans, not those who were smuggled through the southern border,” he said.

In this Daesh publicity image in 2015, a masked militant poses holding the terrorist group's banner somewhere in the deserts of Iraq or Syria. (Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
More than five years since Daesh’s defeat in its last territorial holdout of Baghouz in eastern Syria, many wonder what is drawing new recruits to the group. According to Schmidinger, there is rarely a single reason.
“The biographies of young men who join Daesh are very diverse,” he said.
“These are people who went through strong alienation from their societies. The reasons for this alienation are different. It can be psychological problems, it can be related to racism and anti-Muslim sentiment in Europe, it can be related to the failure of their educational or professional careers. It can be related to problems with their sexual orientation.
“There are different concrete reasons. But what they have in common is this alienation from European societies.”
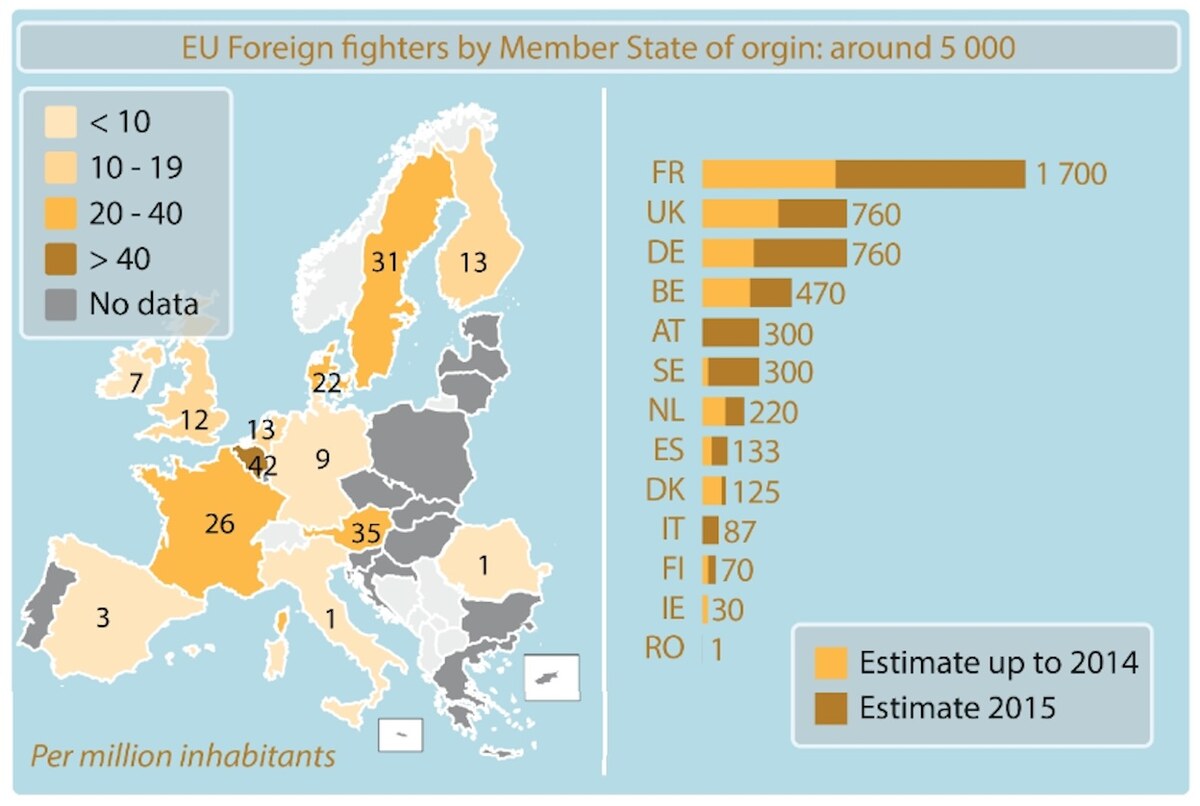
(Source: The Soufan Group, 2014 and 2015/via European Parliamentary Research Service)
He added: “Daesh was here at the moment that they were searching for meaning, belonging and the ability to intervene in history. So you have a lot of people who feel powerless. They have the feeling that by perpetrating, for example, a terrorist attack, or by threatening European societies, they get power. They become masters of their own history.
“Especially for people who feel completely alienated and powerless, this is an attractive opportunity that gives them a kind of empowerment. I think one of the big problems for these people is that there is no other radical but humanistic alternative for them.”
Although Daesh and other extremist entities continue to pose a threat to Western states, there are ways to undermine their attack potential by eliminating their safe havens in the world’s ungoverned and unstable spaces.
Tens of thousands of Daesh-linked individuals are held in prisons and camps across northeast Syria, guarded by the US-backed Syrian Democratic Forces, or SDF. However, these facilities have witnessed frequent violence and escape attempts.
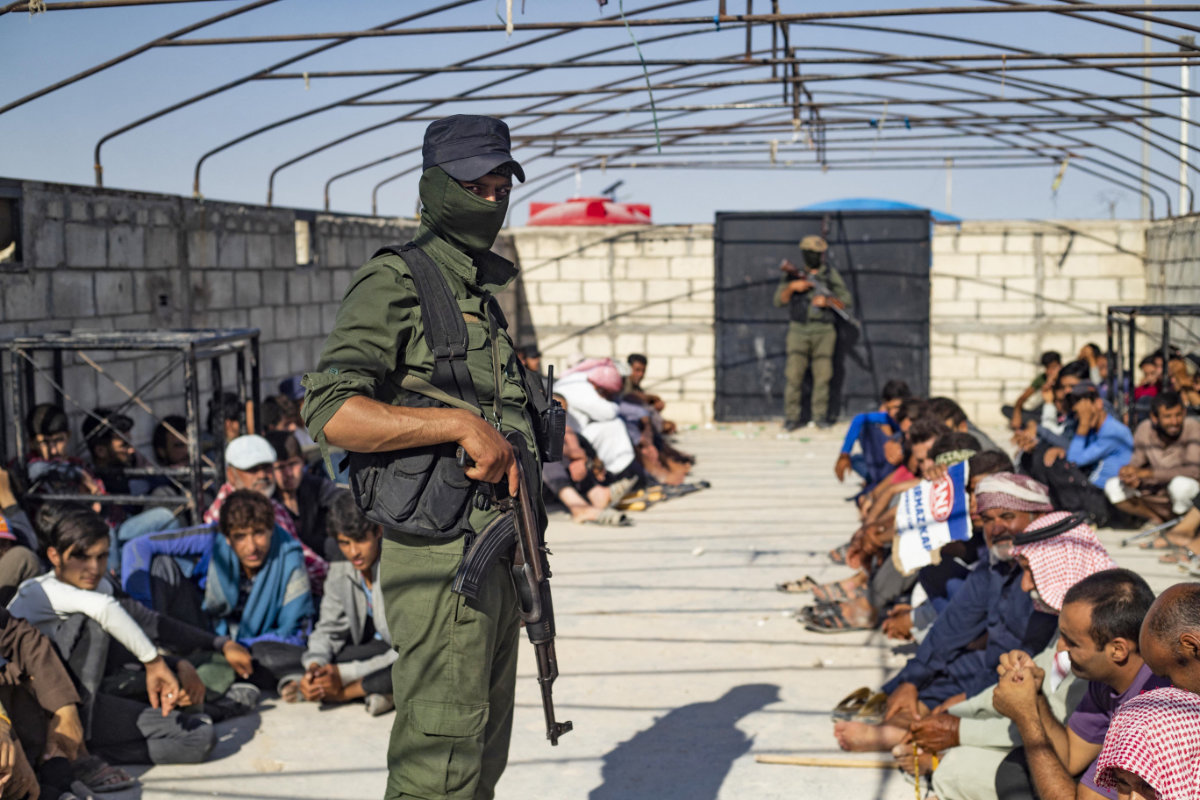

Syrian Kurdish soldiers guard the al-Hol camp in Syria's northeastern Hasakeh governorate, which holds relatives of suspected Daesh fighters. (AFP/File)
Sympathizers in Europe have even organized fundraising campaigns to help Daesh-affiliated women held in these camps to support themselves and even to smuggle themselves out.
Siyamend Ali, a spokesperson for the Kurdish-led People’s Protection Units — a group affiliated with the SDF — told Arab News there are areas of northern Syria where Daesh and other extremist groups “can continue to train, gather resources, issue orders and propagandize.”
Tensions in northeast Syria between the SDF, Syrian regime forces and the Turkish military are also having a destabilizing effect, said Ali, increasing the likelihood of a Daesh resurgence in the region.
In addition to eliminating Daesh’s international networks and safe havens, Schmidinger says that the threat of future attacks in Europe can also be reduced through the implementation of social policies to promote integration and inclusion.
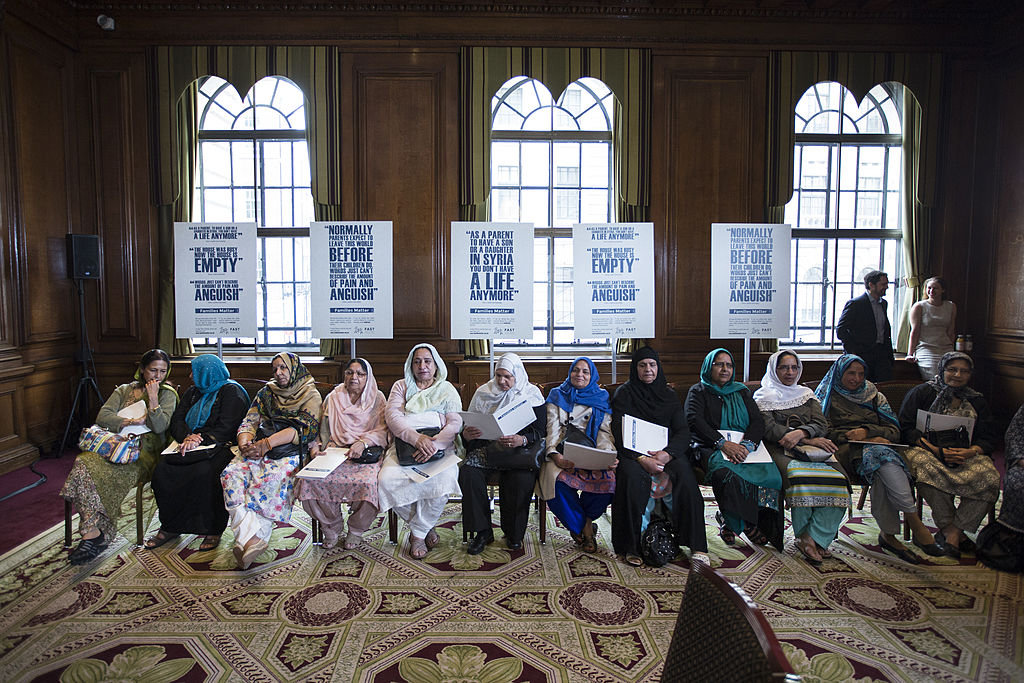

In this photo taken on July 21, 2014, British women wait to attend a gathering in London of the "Families Against Stress and Trauma," which was formed to dissuade young people from traveling to Syria and Iraq to join the Daesh group. (Getty Images)
“You will never be able to completely stop it. We will always face some people on the fringes of society who will be attracted to extremist organizations like Daesh,” he said.
“But it is possible to reduce the number by reducing the feeling of alienation from society. By giving all people the chance for education, a proper job, and to give people — especially young people — the chance to participate in society and politics, it will keep them from feeling that they are powerless and can’t change anything.
“They won’t need an extremist organization to give them the feeling that they can change things in society.”





























