DUBAI: After a string of losses suffered by Hezbollah since the Israel-Hamas war in Gaza began on Oct. 7, Middle East analysts are increasingly asking whether the Iran-backed group has been politically and militarily weakened by the contained conflict in southern Lebanon.
Despite talk of a potential ceasefire in Gaza, there is no guarantee that Israel and Hezbollah will halt their deadly exchanges along Lebanon’s southern border. Nor would it put a stop to the suspected targeted killings of militia leaders deep inside Lebanese territory.
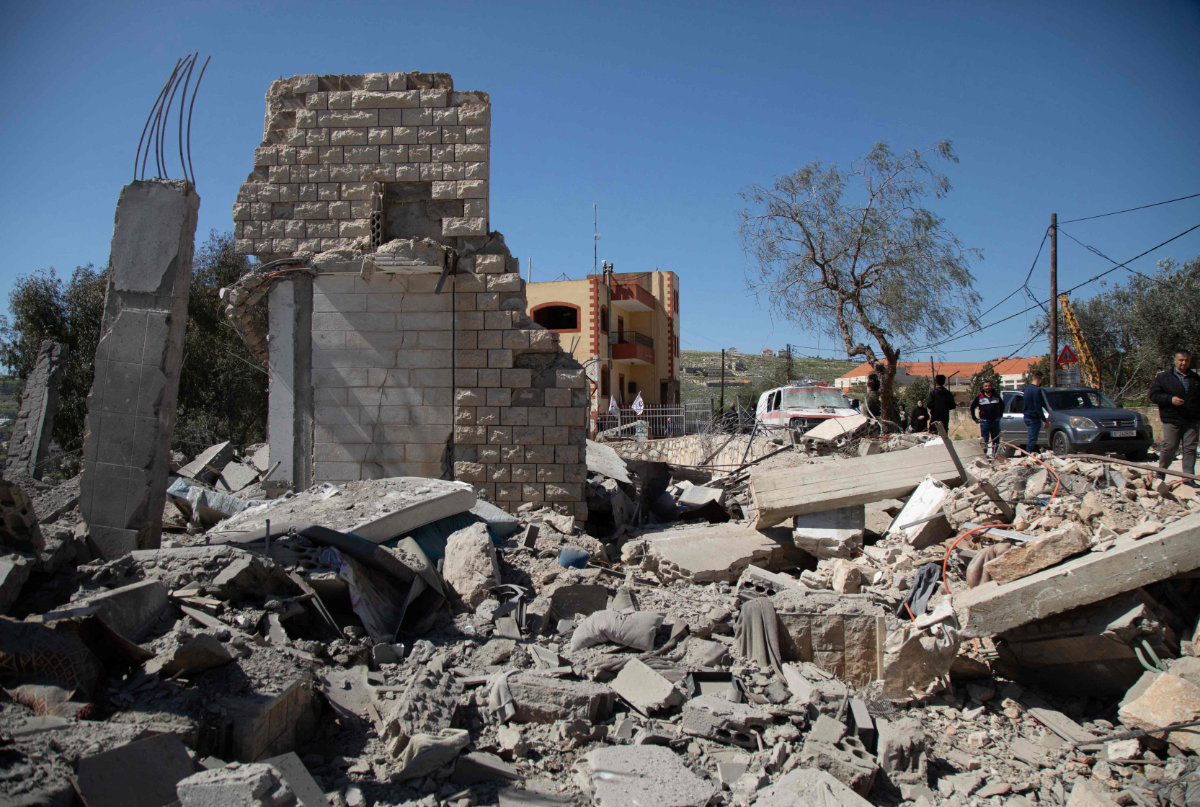

People inspect the site of an Israeli airstrike a day earlier in the southern Lebanese village of Odaisseh near the border with Israel on March 5, 2024. (AFP)
For Lebanon, even this relatively contained tit-for-tat between Israel and Hezbollah has been costly. Civilians living along the border have been killed while thousands have fled north over fears of an Israeli invasion.
On Monday, US envoy Amos Hochstein landed in Beirut in a bid by Washington to reduce regional tensions. His visit coincided with an attack on northern Israel, launched from Lebanon, that left an Indian worker dead and seven others wounded.
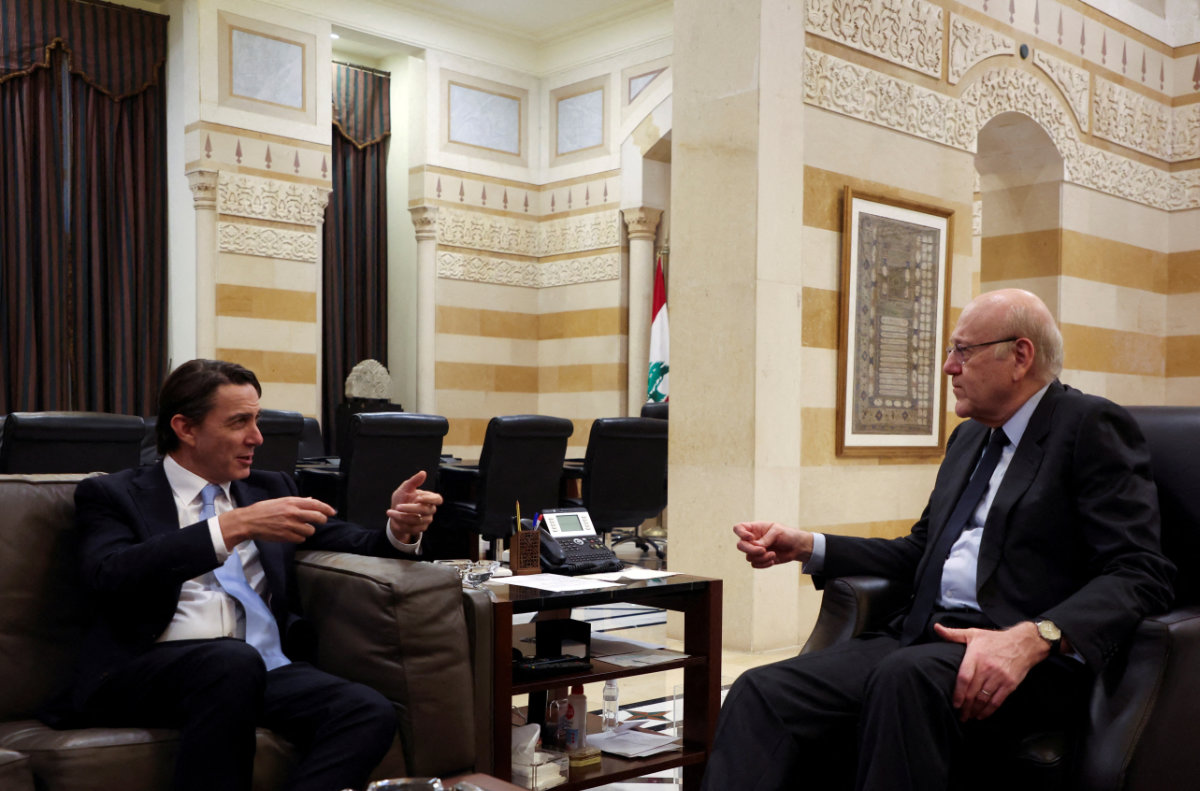

Lebanon's caretaker Prime Minister Najib Mikati (R) meets with US envoy Amos Hochstein in Beirut onn March 4, 2024. (REUTERS)
In a statement during the visit, Hochstein said an escalation “will not help the Lebanese or the Israelis return to their homes. There is no such thing as a limited war; a diplomatic solution is the only way out.”
To achieve “a lasting fair security arrangement between Lebanon and Israel,” Hochstein said “a temporary ceasefire is not enough” and that “a limited war is not containable.”
Security along the Blue Line, demarcated by the UN in 2000 after Israeli troops pulled out of southern Lebanon, “has to change in order to guarantee everyone’s security,” he added.
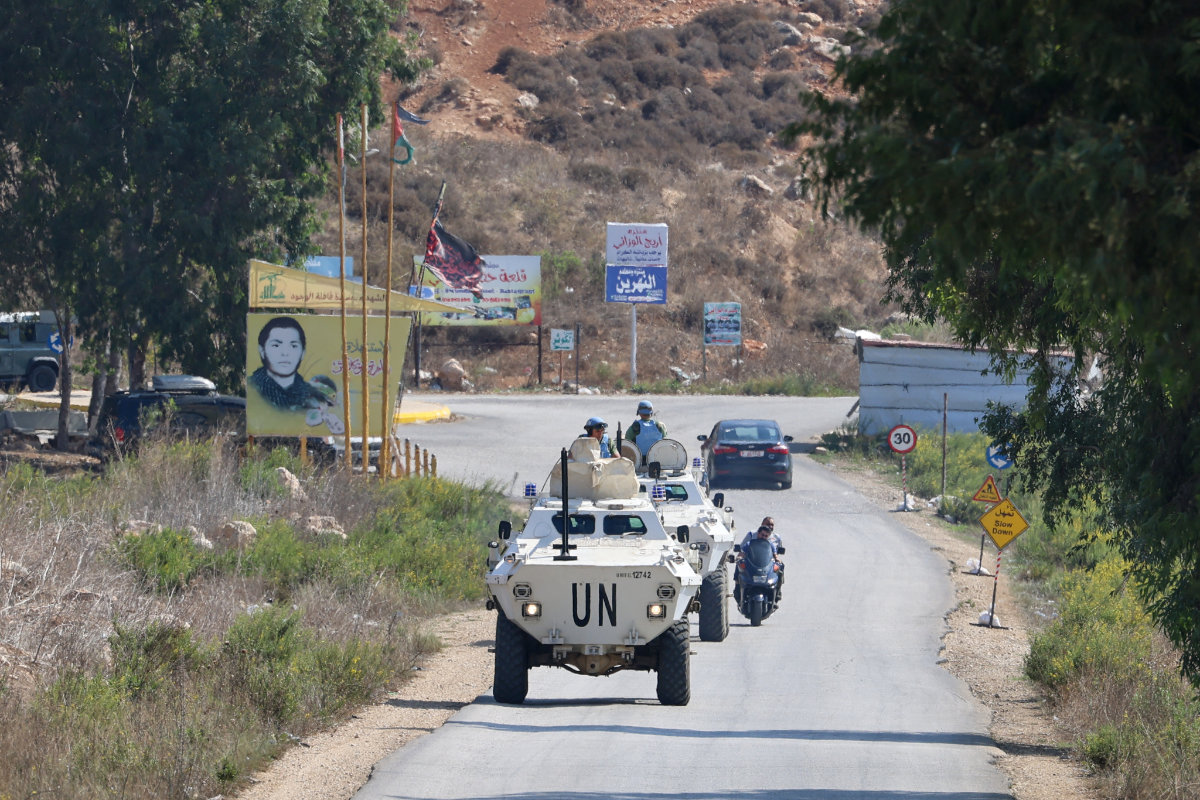

Peacekeepers from the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) patrol the border area between Lebanon and Israel on Hamames hill in the Khiyam area of southern Lebanon, on October 13, 2023. (AFP)
Some analysts believe Hezbollah has done enough to demonstrate support for Palestinians and Hamas, and therefore has nothing more to prove by dragging Lebanon into a major war with Israel.
“It will emerge much stronger and already is stronger internally, because it can claim that it has deterred an Israeli attack,” Nadim Shehadi, former head of the Middle East program at London’s Chatham House, told Arab News.
“If there is no all-out war, then Hezbollah can shut down all the critics of its arms and declare all its opponents as collaborators with the enemy, because they will claim that Hezbollah’s arms protected Lebanon and deterred an attack.
“This is, of course, getting less convincing as Israel escalates, but in the end, they will twist it in their favor.”
INNUMBERS
• 10 Israeli soldiers and reservists killed by Hezbollah and other militia attacks since Oct. 8.
• 229 Hezbollah members killed by Israel, mostly in Lebanon, but some also in Syria.
• 30 Civilians, three of whom were journalists, killed by Israeli strikes on Lebanon.
Although all sides appear keen to avoid a direct military confrontation that could lead to a major regional conflict, there has been no lull in hostilities except as part of the temporary ceasefire in November last year during the Israel-Hamas war.
Speaking on Monday, Hezbollah’s deputy chief, Naim Qassem, reiterated that the militia, which says it is acting in support of Palestinians in Gaza and Hamas, would stop its attacks on Israel once the war in the enclave ends. “Stop the assault on Gaza and war will end in the region,” he said.
However, Yoav Gallant, the Israeli defense minister, has said that there will be no let-up in Israeli operations against Hezbollah even if a Gaza ceasefire is secured.
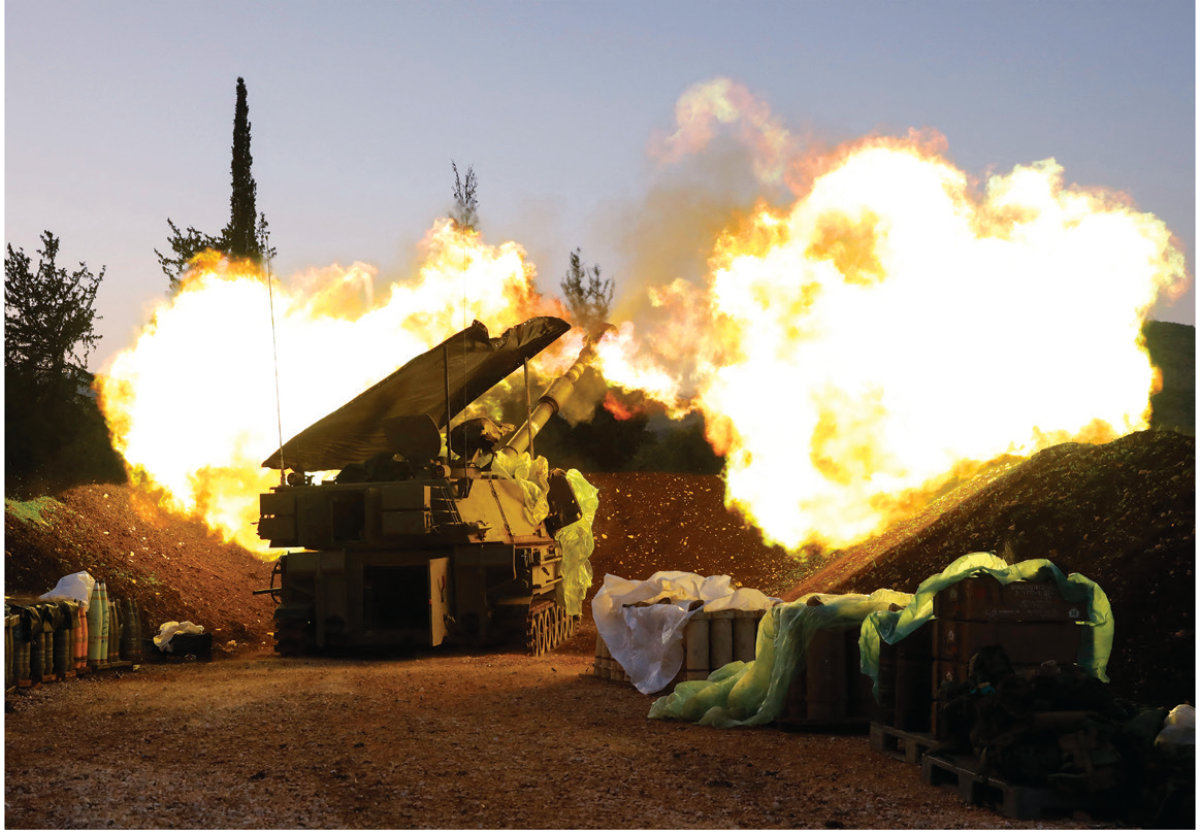

Israel has warned that there would be no letup in its operations against the Hezbollah in Lebanon for as long as they continue to post a threat. (AFP)
Indeed, there is pressure from more hawkish elements in Israel for the government to act decisively against the Hezbollah threat on the country’s northern border. Likewise, Hezbollah is under pressure to ride to the rescue of its Hamas brethren.
There are practical reasons why Hezbollah may be keen to avoid an all-out war with Israel. The availability of weapons, finance for postwar reconstruction and the objectives of Iran could all be key considerations in Hezbollah chief Hassan Nasrallah’s calculations.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Through the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, “Tehran has invested billions of dollars in Hezbollah’s missiles,” Meir Javedanfar, an Israeli lecturer, author and professor of Iranian politics at Reichman University in Israel, told Arab News.
“Their job, their most important priority, is to deter Israel from attacking Iran’s nuclear installations. If Hezbollah gets involved in a war against Israel now, with all those missiles, then Iran’s nuclear program will be left badly exposed.”
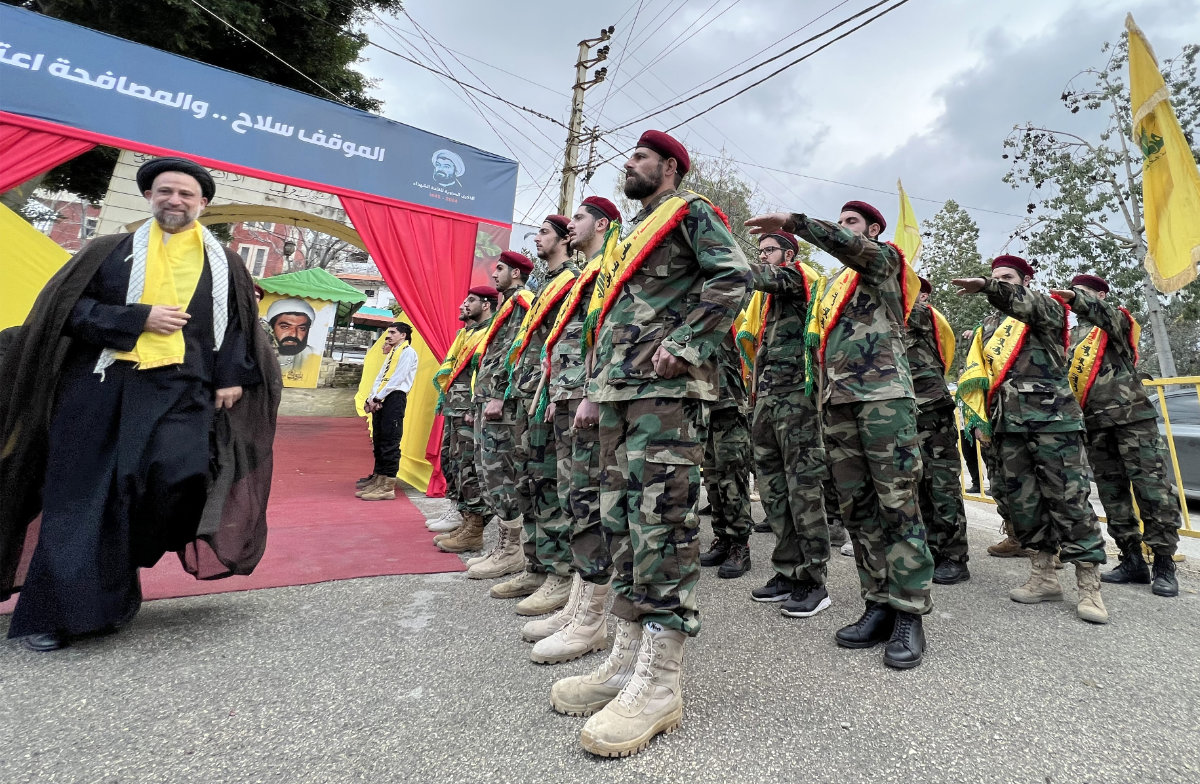

Hezbollah fighters take part in a ceremony to commemorate the party's fallen leaders in the Lebanese village of Jibshit, about 50 kilometers south of the capital Beirut on Feb. 15, 2024. (AFP)
Indeed, no matter how sincere its support for the Palestinian cause, Hezbollah has an incentive to keep its powder dry so it can continue to act as a credible deterrent against a pre-emptive Israeli strike on Iran.
“Another is the fact that if there is a war, this time around Iran cannot pay to rebuild Lebanon back like it did in 2006,” said Javedanfar.
“Iran’s economy is doing terribly now and has been under sanctions since 2012. Iranians won’t be able to pay nor restock Hezbollah’s ammunition, and this will all undermine Hezbollah’s position.”
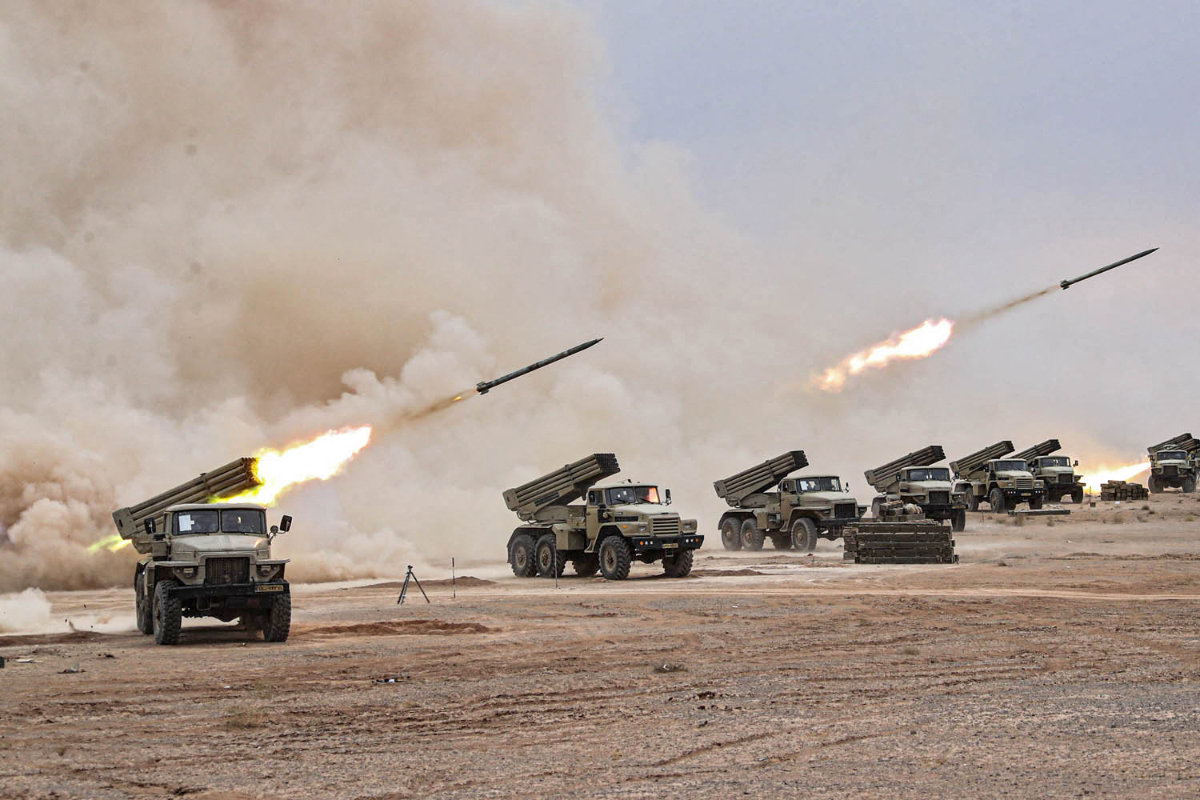

A handout picture provided by the Iranian Army media office on October 27, 2023, shows missiles being fired during a military drill in the Isfahan province in central Iran. (AFP)
Since Hezbollah began its campaign in solidarity with Hamas on Oct. 8, ostensibly to draw Israeli resources away from the Gaza Strip, Israel has launched a series of targeted drone strikes on militia commanders in Lebanon.
Hussein Yazbeck, whose precise rank in the militia is unknown, was killed on Jan. 3. Wissam Hassan Al-Tawil, a commander in Hezbollah’s elite Radwan Force, was assassinated on Jan. 8, while Ali Hussein Burji, aerial forces commander, was killed in southern Lebanon on Jan. 9.
Israel has also struck suspected IRGC and Hezbollah weapons depots and missile launch sites in Lebanon, many of which were situated in residential areas.
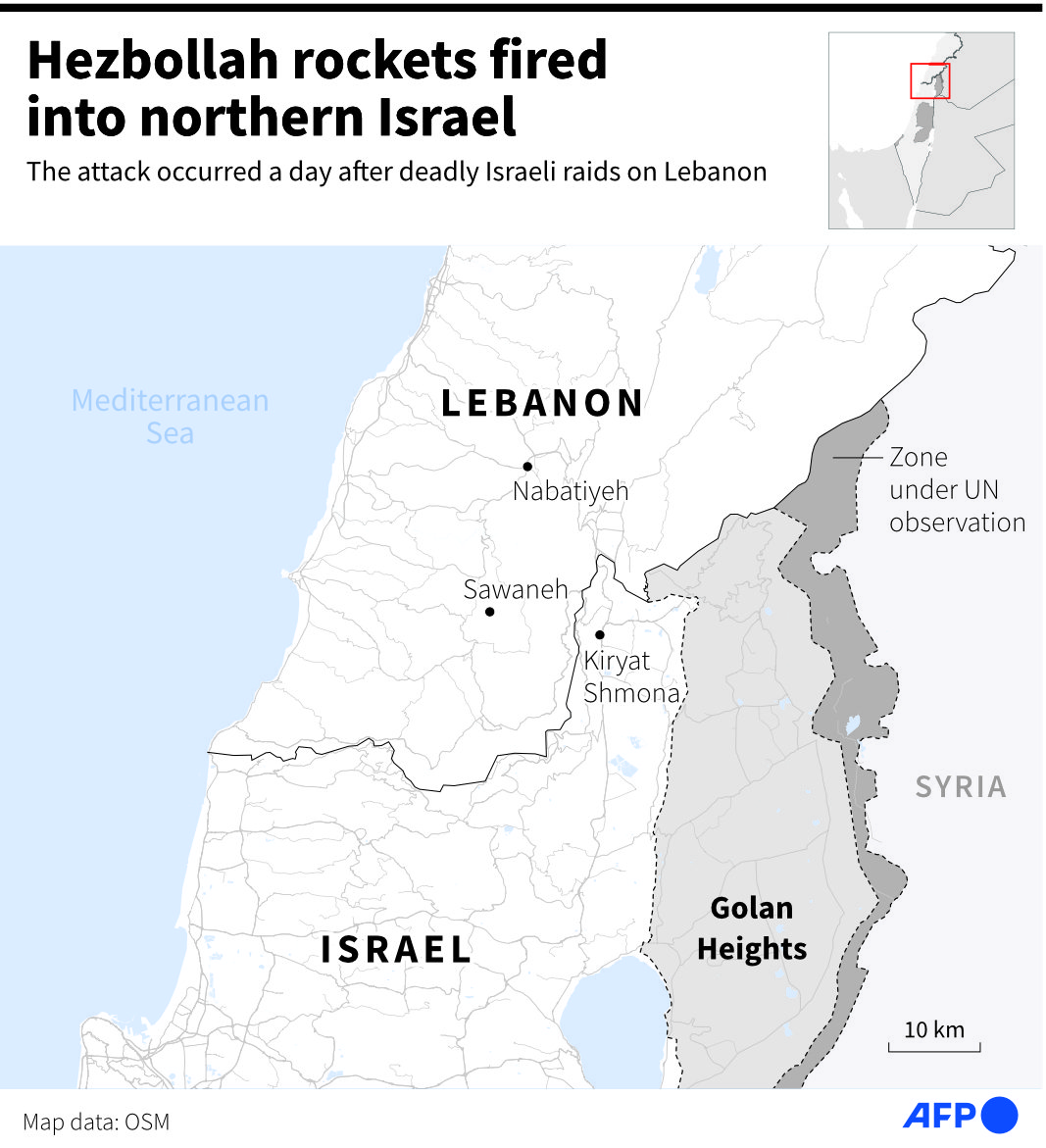
So far, the armed exchanges have resulted in seven civilian deaths on the Israeli side, as well as the deaths of 10 Israel Defense Force soldiers and reservists. There have also been several attacks on Israel from Syrian territory, without any injuries.
Hezbollah has named 229 members who have been killed by Israel, mostly in Lebanon, but some also in Syria. In Lebanon, another 37 operatives from other groups, a Lebanese soldier and at least 30 civilians, three of whom were journalists, have been killed.
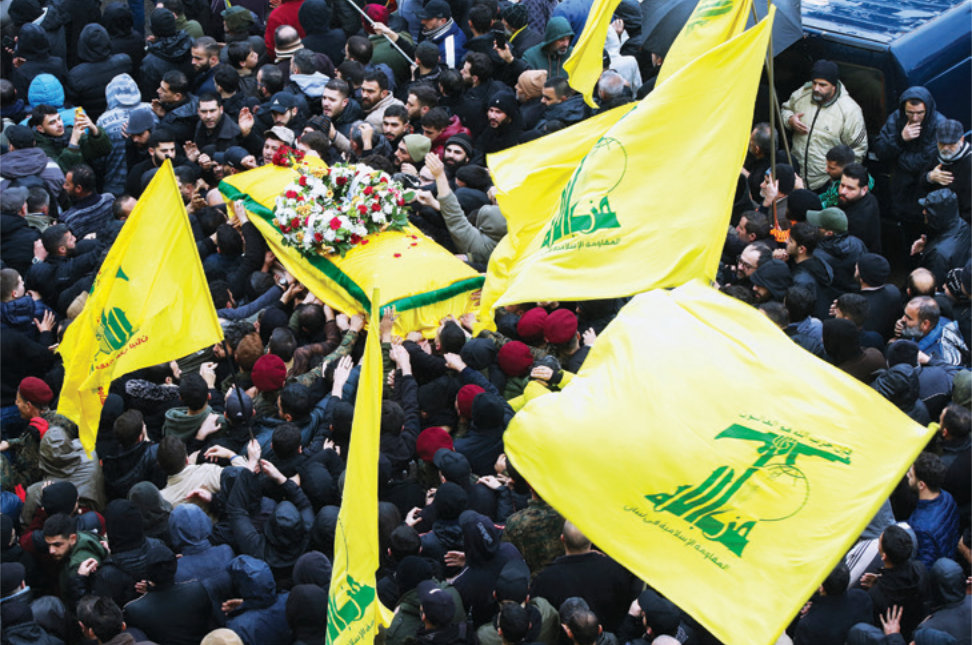

Hezbollah militants and supporters attend the funeral of Ali al-Debs, one of the militant group's commanders killed by an Israeli air raid two days earlier, in Lebanon's southern city of Nabatieyh on February 16, 2024. (AFP)
Lebanese ministers have continued to urge restraint. “At a time where we insist on calm and call on all sides to not escalate, we find the Israeli enemy extending its aggression,” Najib Mikati, Lebanon’s caretaker prime minister, said in a statement last month.
The statement came in response to a deadly Israeli airstrike in Nabatieh, southern Lebanon, which left 10 civilians dead, including seven members of the same family and a mother and her two children. A day of mourning was called in the aftermath of the attack.
Nabih Berri, the speaker of the Lebanese parliament, condemned the “massacre,” adding that “the bloodshed in Nabatieh is on the hands of the international envoys, the UN and human rights organizations” for failing to act to reduce tensions.
Hezbollah, meanwhile, vowed to retaliate for the attack. “The enemy will pay the price for these crimes,” Hassan Fadlallah, a senior Hezbollah official, said in a statement.

Hezbollah supreme leader Hassan Nasrallah is seen on large television screen in Beirut as he delivers a televised address amid the ongoing battles between Israel and the Palestinian group Hamas. (AFP)
Soon after, a barrage of rockets was fired toward a military base in Safed in northern Israel, killing Israeli army Staff Sgt. Omer Sarah Benjo.
Although Hezbollah may have strengthened its position politically in Lebanon, while preserving its strategic advantage on behalf of Iran, there are some who will view the militia’s restraint as a sign of weakness at a time when its Palestinian allies were most in need.
“We don’t want war, but if they (the Israelis) attack us we’ll be sure to attack them back,” Ali Chedid, a resident of Dahiyeh, a predominantly Shiite suburb of Beirut and Hezbollah stronghold, told Arab News.
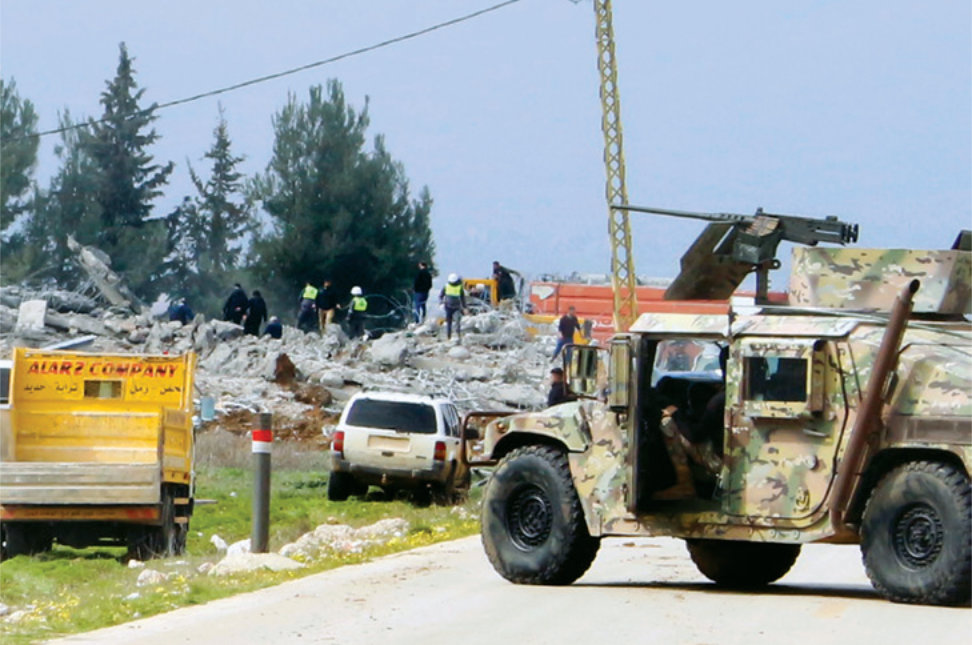

People inspect the damage caused by Israeli bombardment on Hezbollah targets along Israel's. borders with Lebanon. (AFP)
“Hezbollah has been doing a great job of showing restraint so far. It is not a matter of not having enough weaponry or funding to launch a war. Rather it is because we know if we set out to destroy Israel, we also will be destroyed in the process. We never claimed we would remain unscathed.”
For Chedid, the war in Gaza has put Hezbollah in an impossible fix that will be hard for its leaders to navigate if they hope to avoid, at the very least, tarnishing their reputation as champions of the Palestinian cause and the main bulwark against Israel.
“Hezbollah is damned if it attacks because then people will claim it is dragging the country into war for its own interests,” said Chedid. “It is also damned if it doesn’t because it will be accused of being all smoke and mirrors and having left Gazans to suffer alone.”































